Visited Companies





1️⃣ Company Snapshot
Visa China (维萨中国)
- Entered China: 1993 · HQ: Shanghai / Beijing
- Partners with Chinese banks to issue Visa-branded debit and credit cards, often with dual-currency (RMB + USD) functionality for international use.
- Enables secure cross-border payments for Chinese consumers, businesses, and students, especially in travel, overseas shopping, and education.
- 🔗visa.com.cn
- 📌“Connecting China to the global economy through trusted digital payments”
2️⃣ Why This Company Matters to SEE China
Visa China plays a critical role in bridging China’s domestic financial ecosystem with the world. In a landscape dominated by mobile-native platforms like Alipay and WeChat Pay, Visa operates in complementary spaces—international travel, cross-border online shopping, and partnerships with global brands. It offers insight into how foreign financial institutions operate under local regulations, adapt to Chinese consumer behavior, and contribute to China’s outbound digital commerce.
3️⃣ Industry Context & Comparison
Dimension | Visa China (维萨中国) | Alipay / WeChat Pay |
Core Use | Cross-border card payments, international e-commerce | Domestic everyday payments, P2P transfers |
Form Factor | Physical & virtual cards, tokenized wallets | QR code, app-based payments |
Key Users | International travelers, students, business clients | Urban consumers, small vendors, digital natives |
4️⃣ Student Field Highlights
📷 Photos: QR-payment demo / Visa wallet integrations / fintech partner logos
💬 Quote: “Visa isn’t just a card—it’s a protocol for how money moves globally.”
5️⃣ Student Takeaways
“Visa taught me that American payment systems are global even when invisible.”
“I didn’t know Visa was involved in blockchain and central bank digital currencies.”
“Seeing the contrast with Alipay and WeChat Pay helped me understand platform thinking.”
6️⃣ Explore More
- 📄 Related: “The Global Payment Race: Card Rails vs. Super Apps”
- 🔁 Compare with: Alipay + WeChat Pay (Tencent)
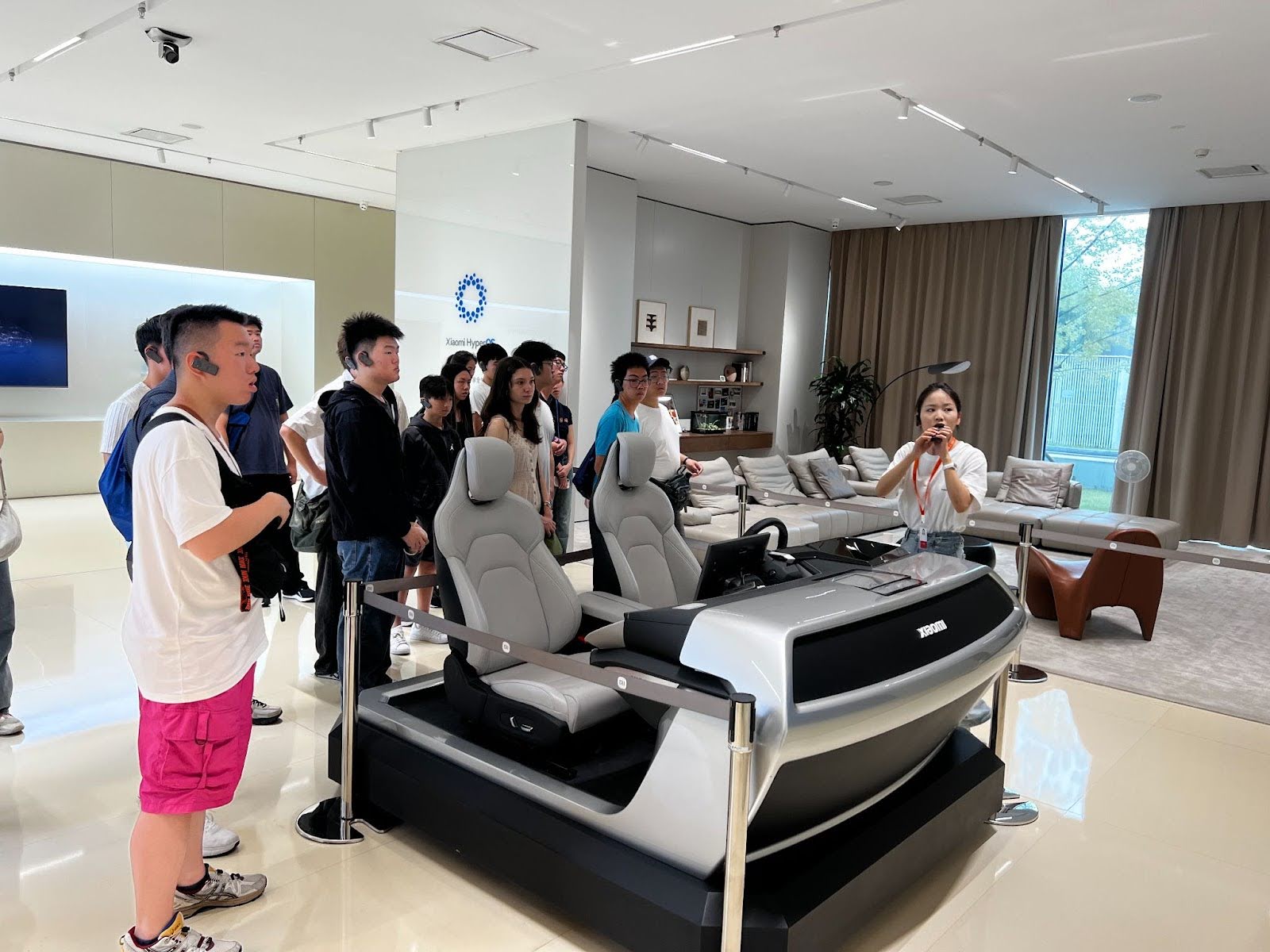






1️⃣ Company Snapshot
Xiaomi Corporation 小米科技
- Founded: 2010 · Headquartered in Beijing, China
- Global smartphone leader and smart ecosystem powerhouse, with $38 billion in 2023 revenue and a $50 billion market cap
- Operates the world’s third-largest smartphone brand, linking 700M+ smart devices across its AIoT ecosystem
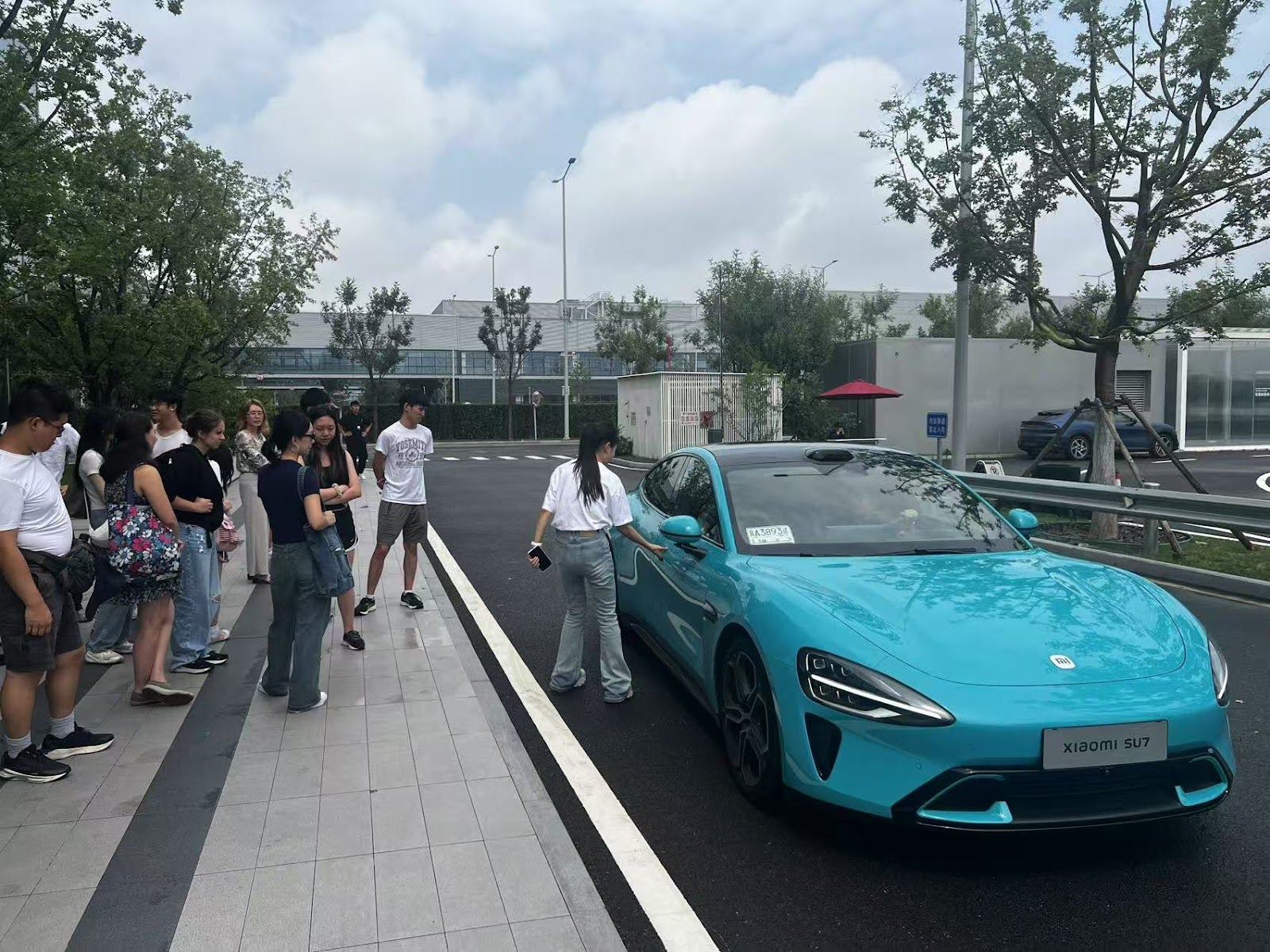
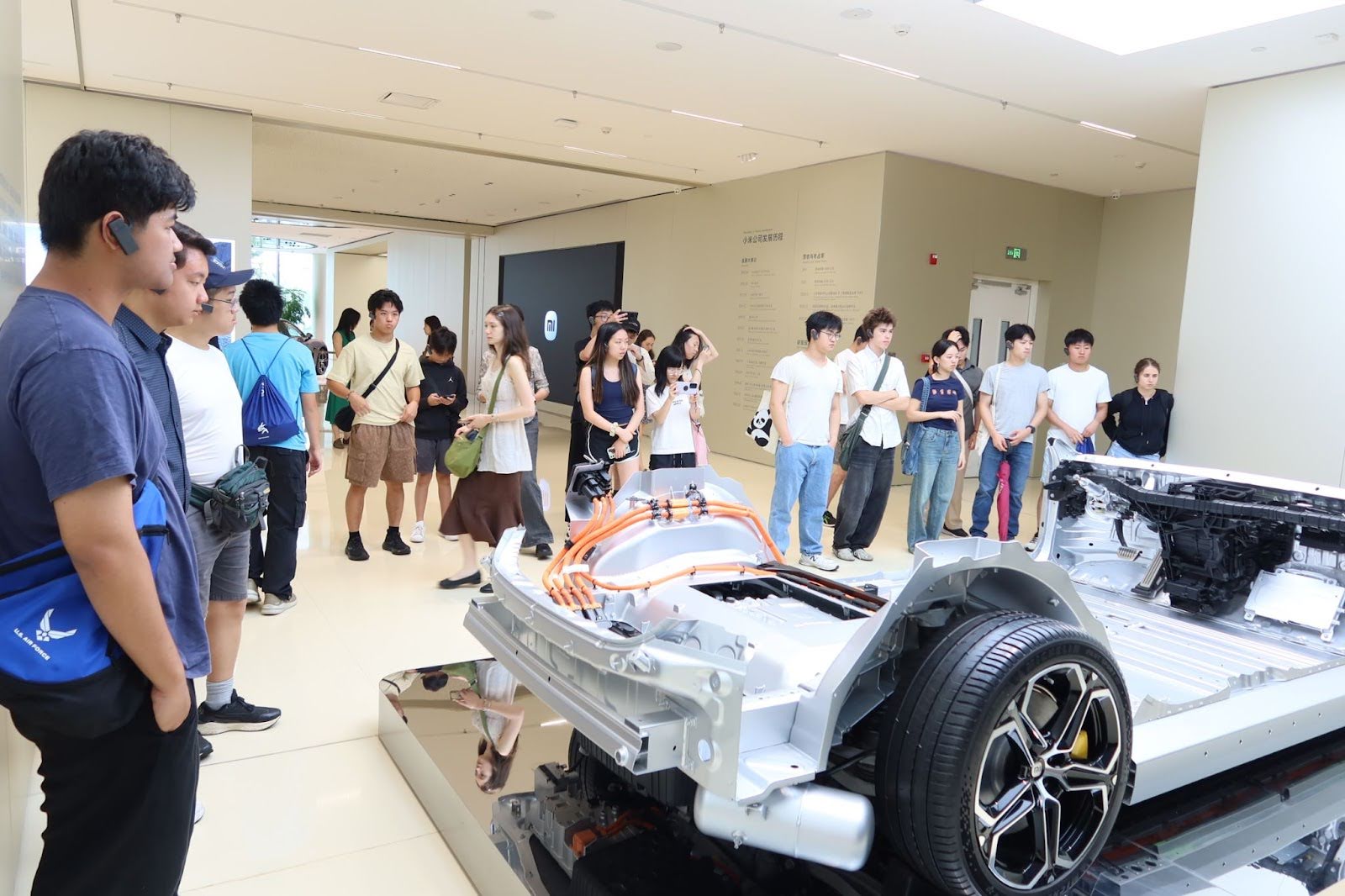
- Expanding into electric vehicles (SU7 sedan), robotics, smart homes, wearables, and generative AI
- 🔗 https://www.mi.com
- 📌 “From budget phones to smart everything—Xiaomi redefines Chinese tech”
2️⃣ Why This Company Matters to SEE China
Xiaomi symbolizes China’s evolution from a manufacturing hub to a global innovator. Through its smart ecosystem, affordable high-tech products, and expansion into electric vehicles, Xiaomi embodies national strategies in AIoT, industrial automation, and green tech. It’s a case study in how Chinese firms leverage scale, speed, and system-level design to compete globally.
3️⃣ Industry Context & Comparison
Key Driver | China (Xiaomi) | U.S. Counterpart (Tesla / Apple EV Project) |
Productivity + Market Reform | Smart EV plant with 700+ robots and autonomous mobile robots; AI-driven quality control; 1 car/76 sec | Tesla is advanced but less vertically integrated; Apple EV slowed by regulatory drag |
Long-Term Strategic Planning | NDRC/MIIT-approved, subsidy-backed; aligns with China’s national EV + smart tech goals | Apple EV uncertain; U.S. faces decentralized EV policies and inconsistent incentives |
Institutional Advantage | Speedy land acquisition, policy support, and automation scaling through public-private coordination | U.S. firms often hindered by fragmented governance and slower industrial scaling |
4️⃣ Student Field Highlights
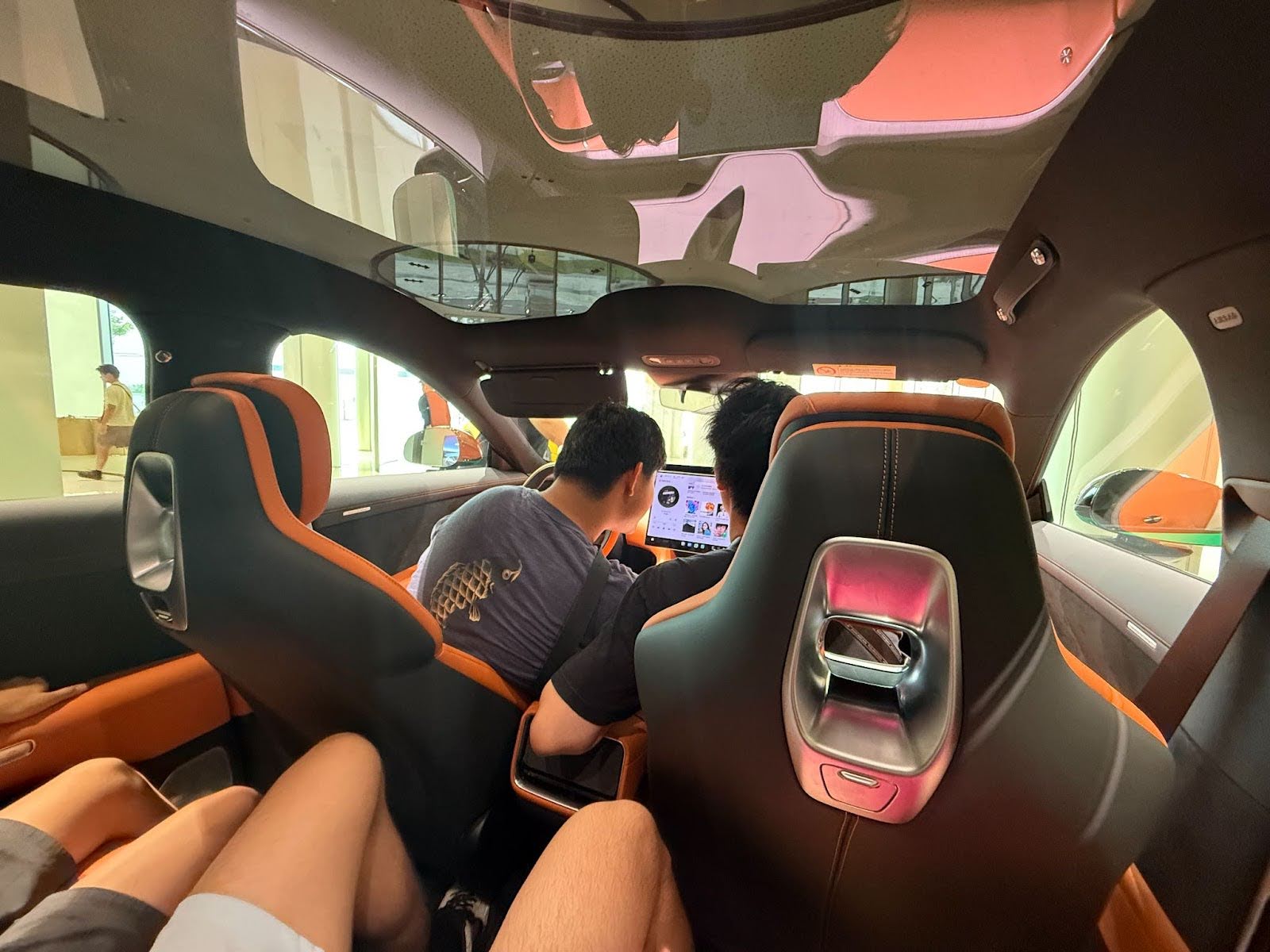
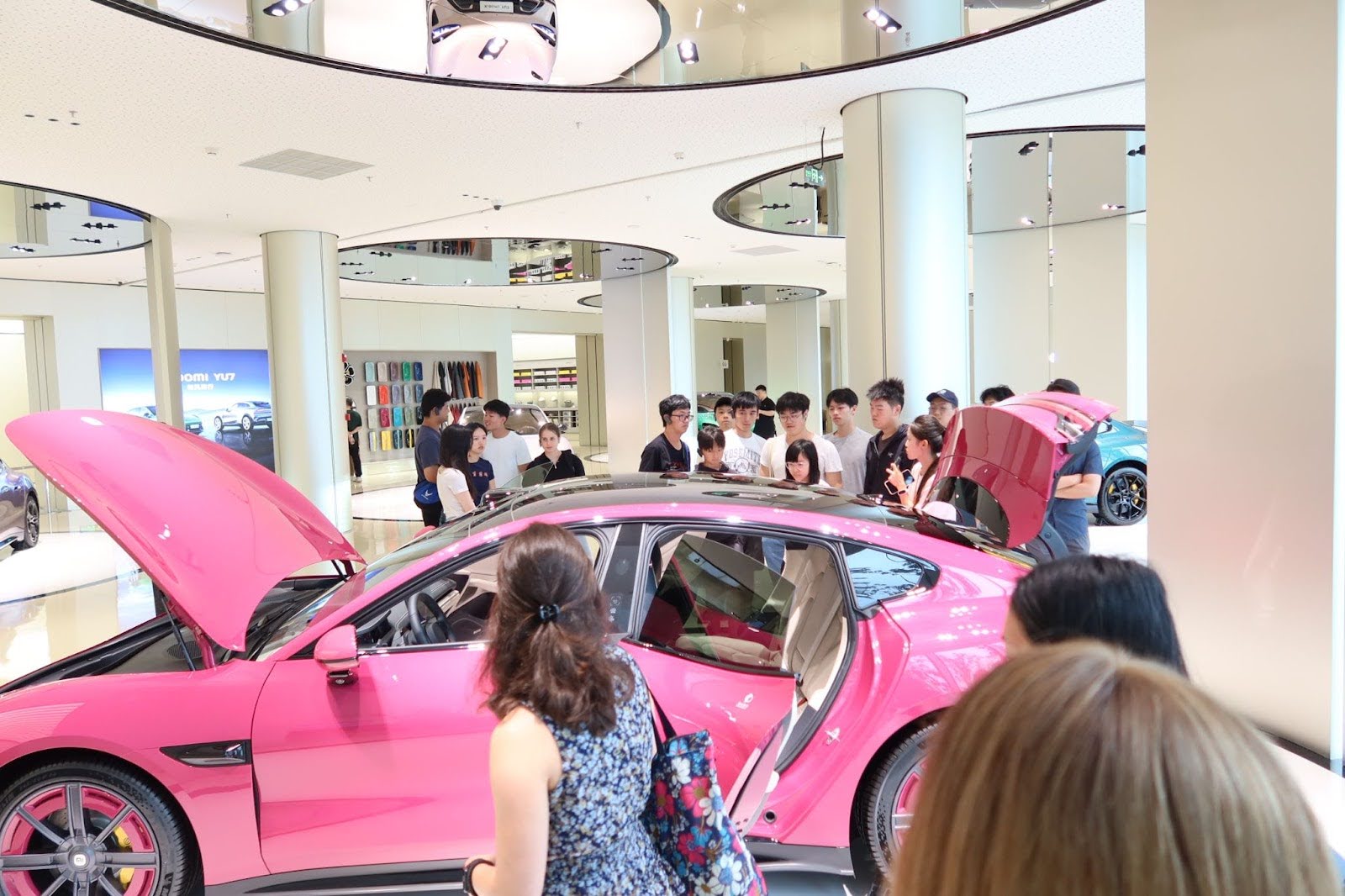
📷 Photos: EV assembly line / smart home integration demo / Xiaomi AI dashboard
💬 Quote: “We came for the EVs, but left realizing Xiaomi is building an entire digital lifestyle.”
5️⃣ Student Takeaways
“Xiaomi’s EV plant was like stepping into a sci-fi movie—it’s fast, precise, and fully connected.”
“Seeing a car talk to a smart home system was wild—Xiaomi’s ecosystem thinking is years ahead.”
“This isn’t just about phones; Xiaomi is showing us what a unified tech future could look like.”
6️⃣ Explore More
- 📄 Related: “AIoT in China: How Platforms Power Everyday Life”
- 🔁 Compare with: Tesla (EV) + Apple (ecosystem & device strategy)






1️⃣ Company Snapshot
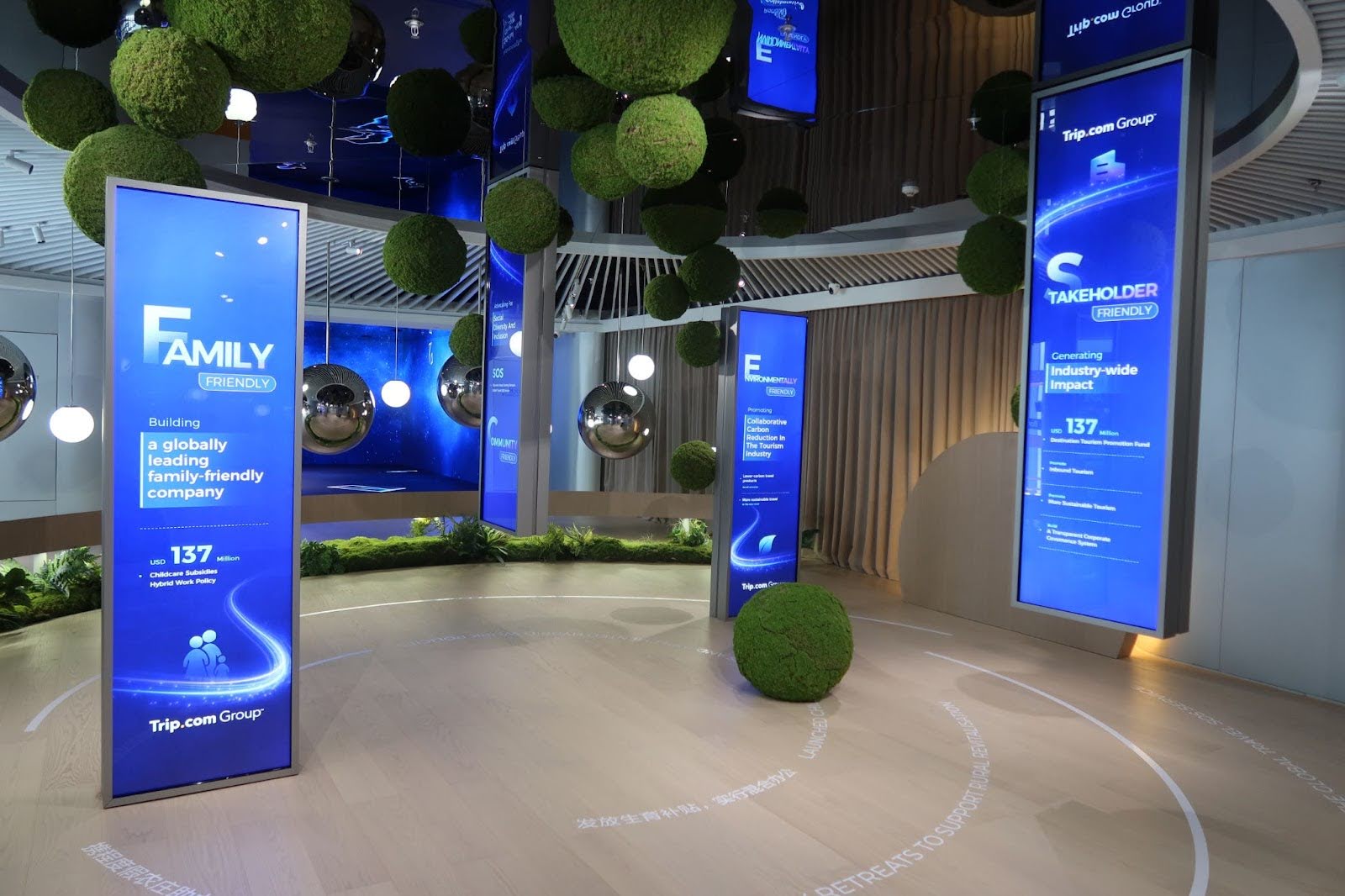
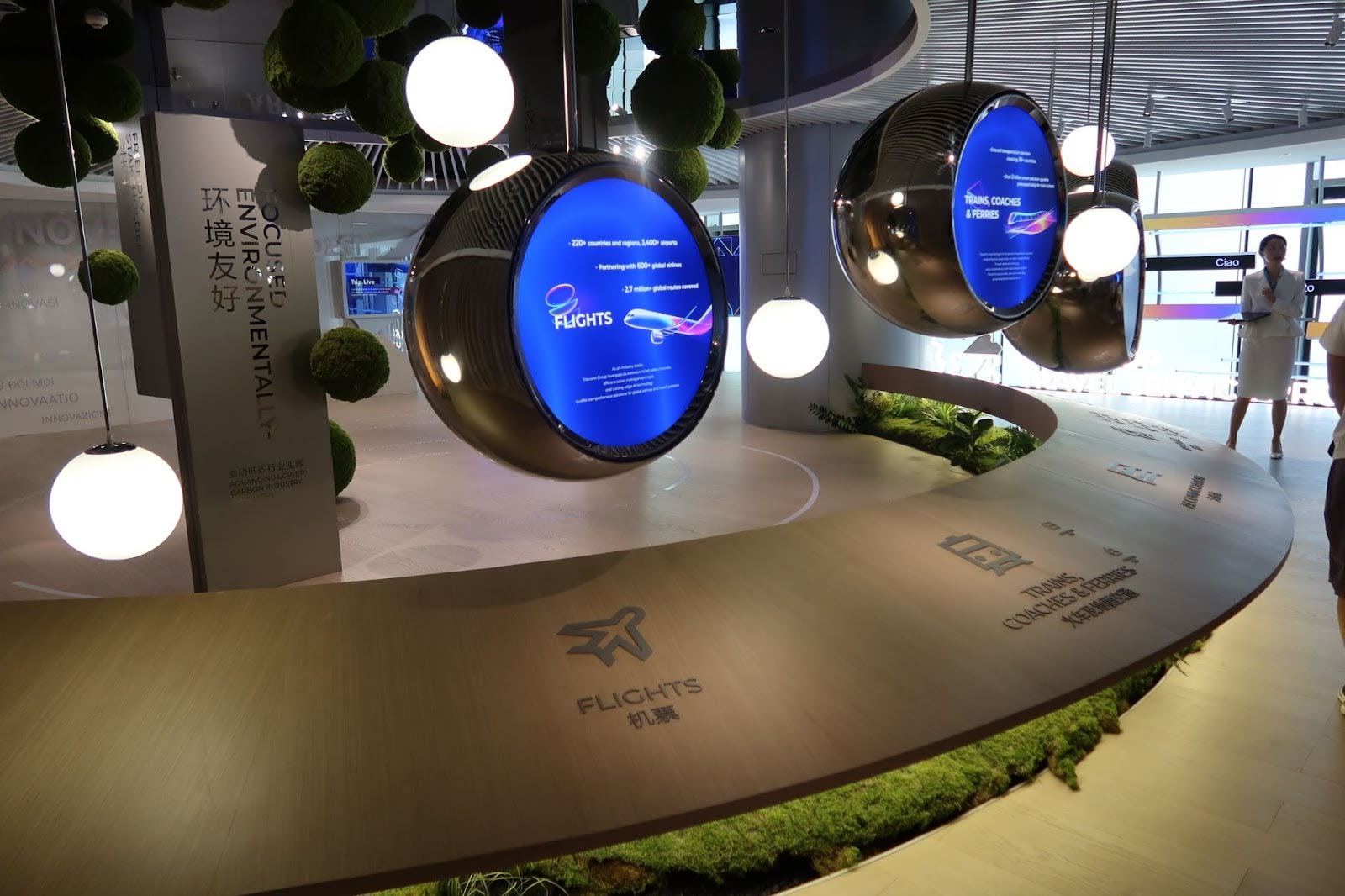
Ctrip (Trip.com Group) 携程集团
- Founded: 1999 · Headquartered in Shanghai, China
- 2023 Revenue: $6.3 billion · Net Profit: $1.4 billion · Market Cap: $33 billion
- One of the world’s largest online travel platforms, with rapid growth—Q3 2024 EBITDA reached 78% of Expedia’s and 32% of Booking’s
- Offers end-to-end travel services powered by AI travel assistants and livestream e-commerce
- 🔗 https://www.trip.com
- 📌 “Digitally enabling China’s rise in global tourism and services”
2️⃣ Why This Company Matters to SEE China
Ctrip exemplifies China’s strategic shift from goods manufacturing to global services leadership. It leverages advanced AI, deep platform integration, and China’s massive domestic travel market to scale inbound tourism and export cultural influence. Its digital innovation in travel reflects broader national economic transformation goals.
3️⃣ Industry Context & Comparison
Key Driver | China (Ctrip / Meituan) | U.S. (Expedia / DoorDash / Instacart) |
Productivity + Market Reform | Integrated travel, food, and local services platform reducing friction, improving cost and user trust | Disjointed platforms with higher transaction costs, fragmented services, and less transparency |
Human Capital + STEM Development | AI-driven supply-demand forecasting, dispatch, and user modeling powered by coordinated STEM talent pool | AI use fragmented across firms, typically focused on single verticals without systemic scale |
Institutional Advantage | Strong regulatory support enables platform integration and scalability | Fragmented regulatory landscape and competitive market limits integration and scale |
4️⃣ Student Field Highlights
📷 Photos: AI trip planning demo / livestream e-commerce session / Shanghai HQ tour
💬 Quote: “Ctrip showed us that behind every smooth trip is a complex AI engine working in real-time.”
5️⃣ Student Takeaways
“Seeing AI used for dynamic pricing and trip planning was eye-opening.”
“Ctrip’s human customer support contrasts sharply with the US’s mostly self-service approach.”
“The scale of China’s domestic travel market and government backing really powers their growth.”
6️⃣ Explore More
- 📄 Related: “Digital Transformation of Global Travel Platforms”
- 🔁 Compare with: Expedia + Booking.com + DoorDash + Instacart






1️⃣ Company Snapshot
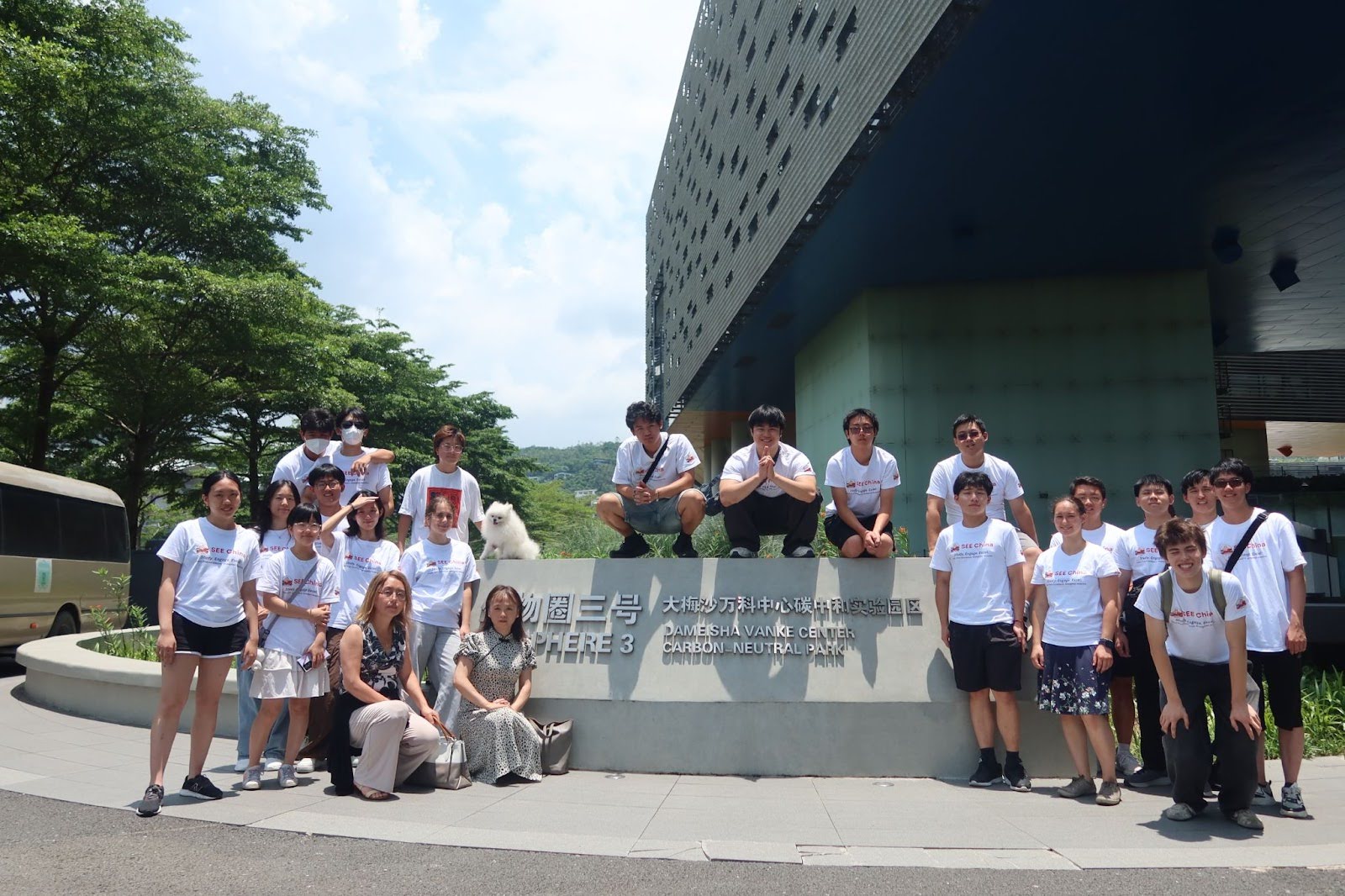
Vanke 万科企业股份有限公司
- Founded: 1984 · Headquartered in Shenzhen, China
- 2023 Revenue: $55.6 billion
- China’s leading residential and mixed-use real estate developer, pioneering sustainable urban projects like Biocity Biosphere No.3
- Blends green architecture, smart city tech, and biophilic design aligned with national “dual carbon” goals
- 🔗 https://www.vanke.com
- 📌 “Building eco-friendly, smart urban communities for China’s sustainable future”
2️⃣ Why This Company Matters to SEE China
Vanke exemplifies how China integrates real estate development with national urban sustainability strategies. Its Biocity project serves as a system-level pilot for scalable, eco-conscious urban living—showcasing coordinated policy support and cutting-edge smart sensing and AI technology for resource-efficient cities.
3️⃣ Industry Context & Comparison
Key Driver | Vanke Practices | Google’s Green Campus |
Productivity + Market Reform | Integrated IoT systems optimize energy and resource use across entire urban areas | Focused on isolated zones, limited integration with broader urban infrastructure |
Long-Term Strategic Planning | Fully aligned with China’s “dual carbon” and “sponge city” policies | Decentralized efforts, fragmented sustainable urban planning |
Institutional Advantage | Top-down national policies enable coherent multi-sector urban sustainability | Lacks centralized coordination, resulting in fragmented approaches |
4️⃣ Student Field Highlights
📷 Photos: Biocity architecture / smart sensing demos / green infrastructure
💬 Quote: “Vanke showed us how urban development and ecology can truly coexist.”
5️⃣ Student Takeaways
“Vanke’s integration of AI and sustainability in real estate is groundbreaking.”
“The top-down policy alignment really speeds up large-scale green urban projects.”
“Seeing Biocity helped me understand the difference between systemic city planning and isolated experiments.”
6️⃣ Explore More
- 📄 Related: “Smart Cities and Dual Carbon Goals in China”
- 🔁 Compare with: Google Green Campus + U.S. Sustainable Urban Projects
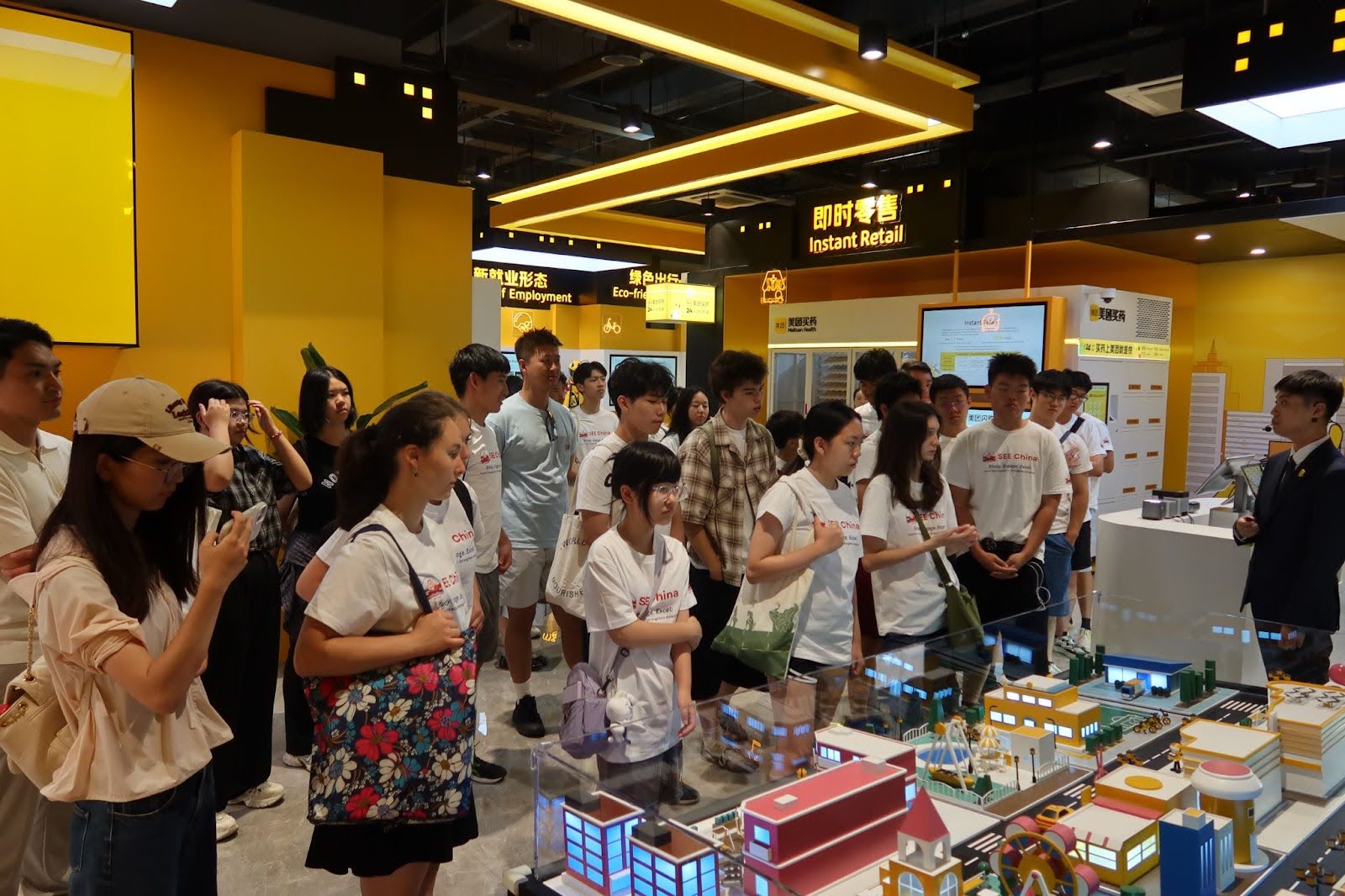
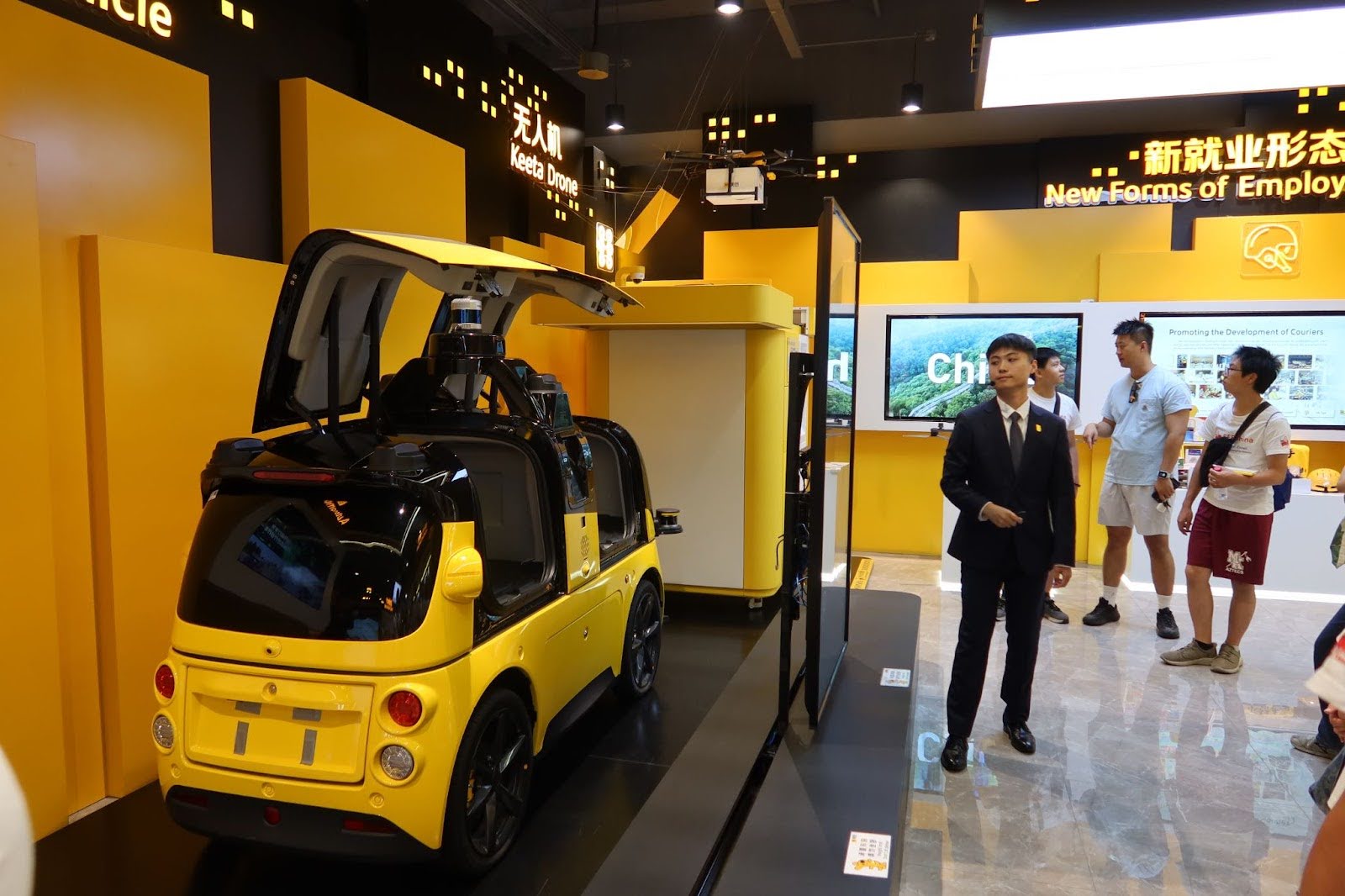
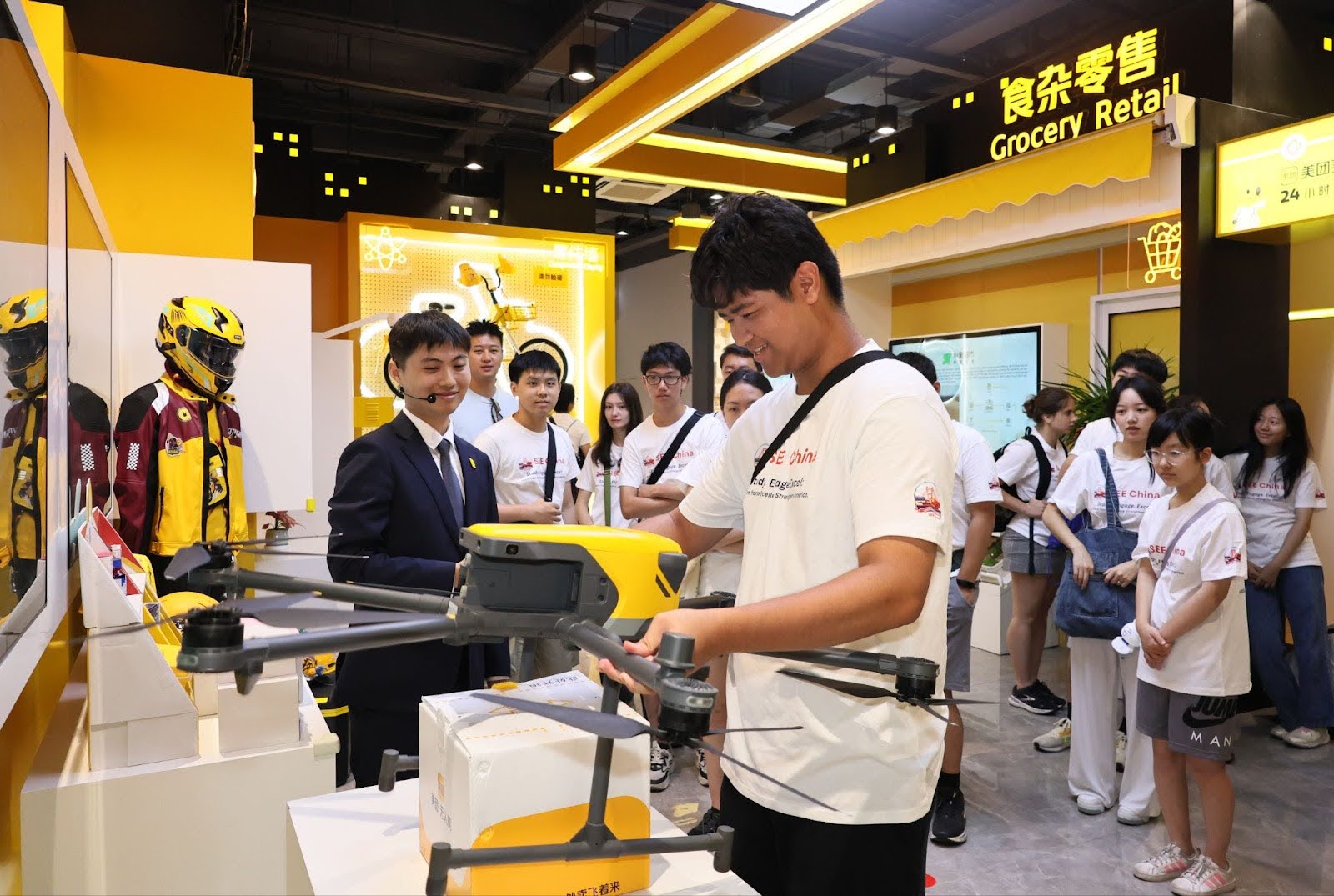
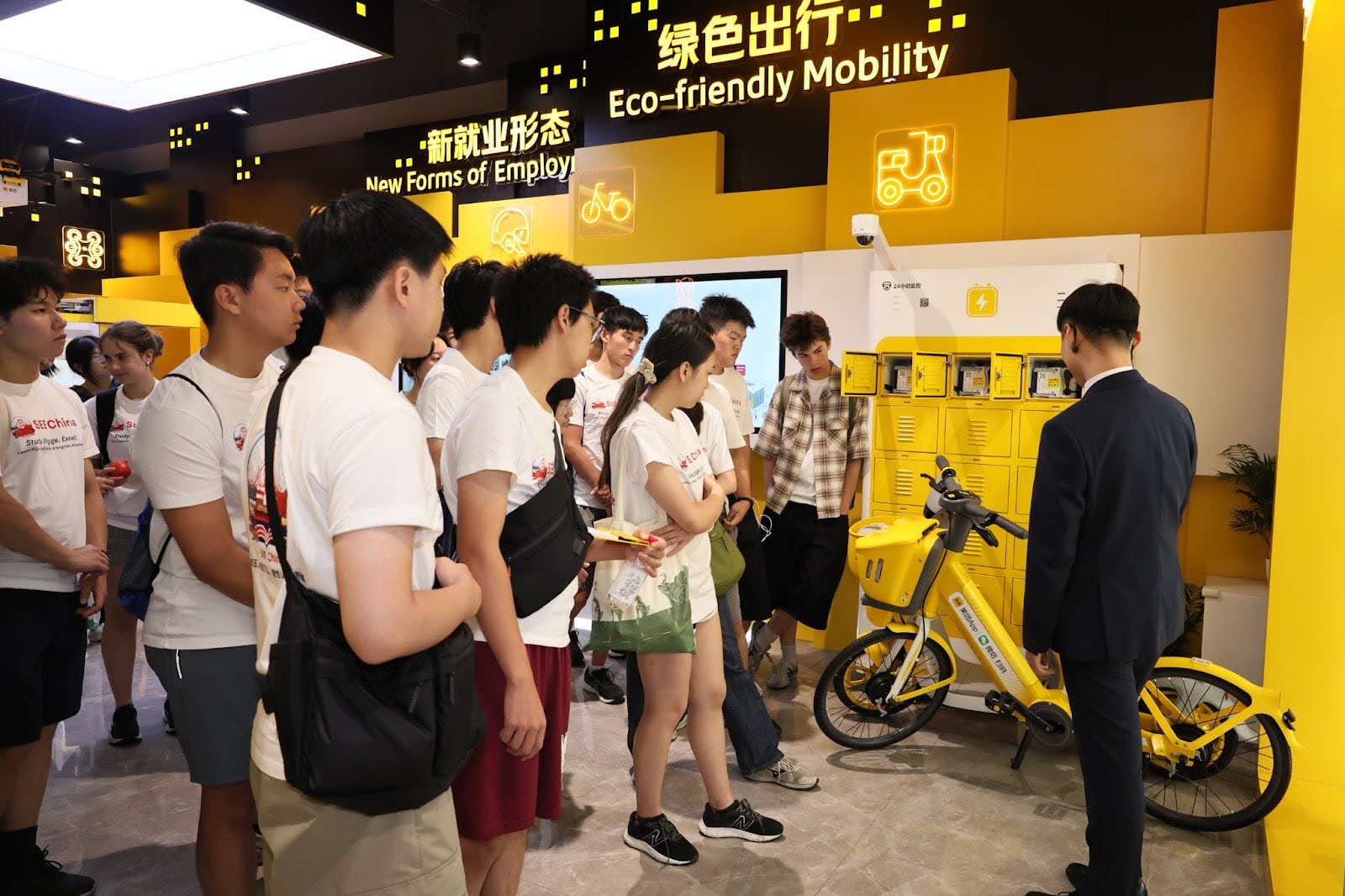
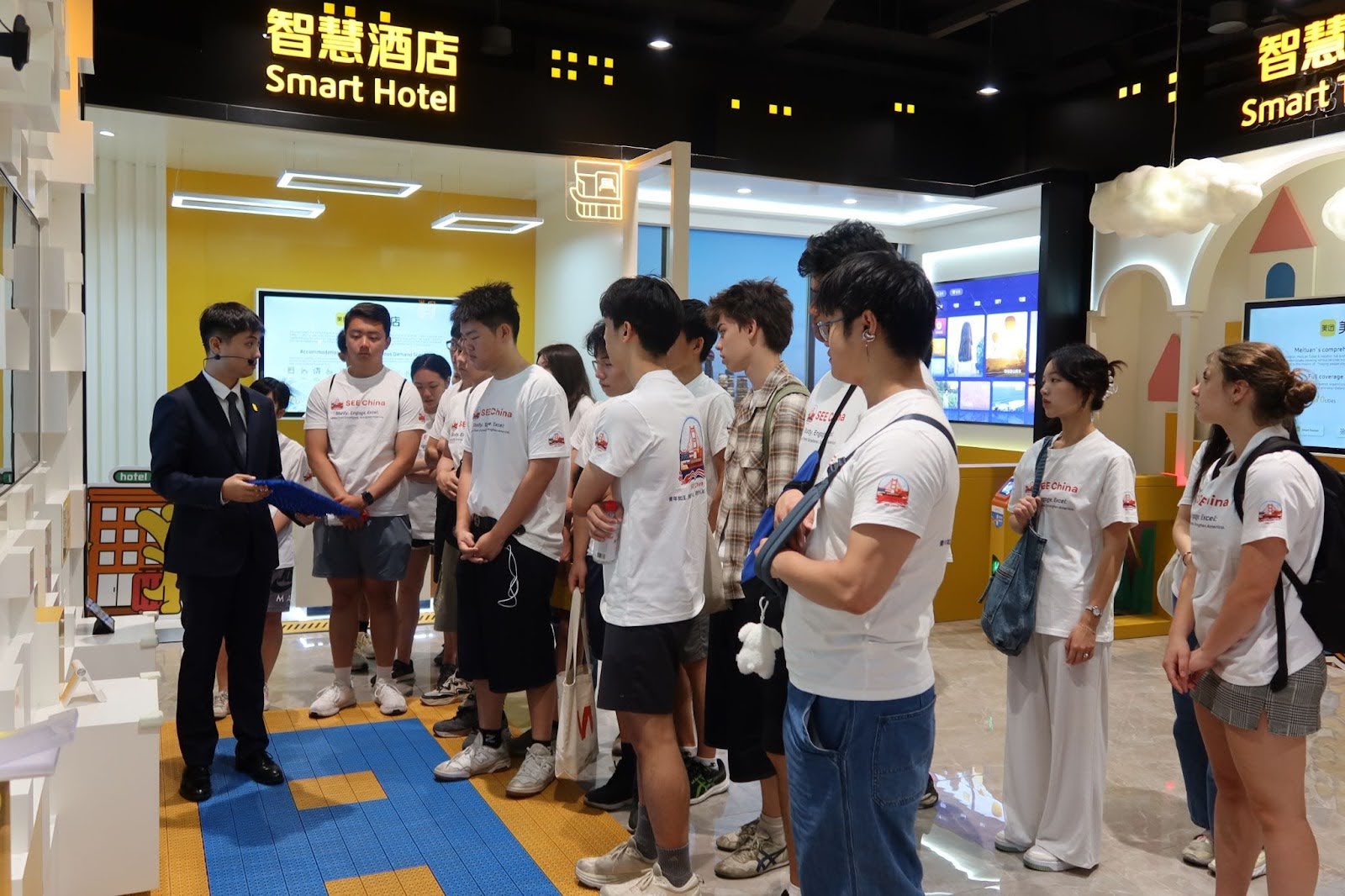






1️⃣ Company Snapshot
Meituan 美团
- Founded: 2010 · Headquartered in Beijing, China
- 2023 Revenue: $35 billion · Market Cap: $100+ billion
- China’s top on-demand services super-app, handling over 80 million daily orders from 500 million annual active users
- Dominates food delivery with 70% market share, also covers local commerce, lifestyle services, and AI-driven logistics
- Pioneering autonomous delivery drones, self-driving vehicles, and AI recommendation engines
- 🔗 https://about.meituan.com
- 📌 “The city operating system that powers China’s urban digital life”
2️⃣ Why This Company Matters to SEE China
Meituan exemplifies China’s digital urban infrastructure under the “Digital China” strategy. Its super-app ecosystem integrates diverse daily services seamlessly, reflecting how commercial platforms evolve into essential infrastructure. The company also showcases AI-driven logistics innovation and strong penetration in lower-tier cities enabled by policy support.
3️⃣ Industry Context & Comparison
Key Driver | China (Meituan) | U.S. (DoorDash / Instacart) |
Productivity + Market Reform | Platform-wide integration reducing friction/cost; transparent pricing; instant feedback | Disjointed platforms with higher costs, less transparency, and fragmented experience |
Human Capital + STEM Development | Leading AI for dispatch, forecasting, user modeling; coordinated STEM talent at scale | AI fragmented across firms, typically single vertical focus without systemic integration |
Institutional Advantage | Supportive digital policies enable deep integration and affordability | Fragmented regulatory and competitive environment limiting scale and integration |
4️⃣ Student Field Highlights
📷 Photos: Drone delivery demo / autonomous vehicle / Meituan super-app UI
💬 Quote: “The integration of food delivery, shopping, and AI logistics is seamless and impressive.”
5️⃣ Student Takeaways
“Meituan’s use of drones and self-driving cars felt like the future of urban logistics.”
“The super-app model makes daily tasks feel effortless and connected.”
“Policy support and STEM talent coordination are key to Meituan’s success in lower-tier cities.”
6️⃣ Explore More
- 📄 Related: “Super-apps and Urban Digital Infrastructure in China”
- 🔁 Compare with: DoorDash + Instacart
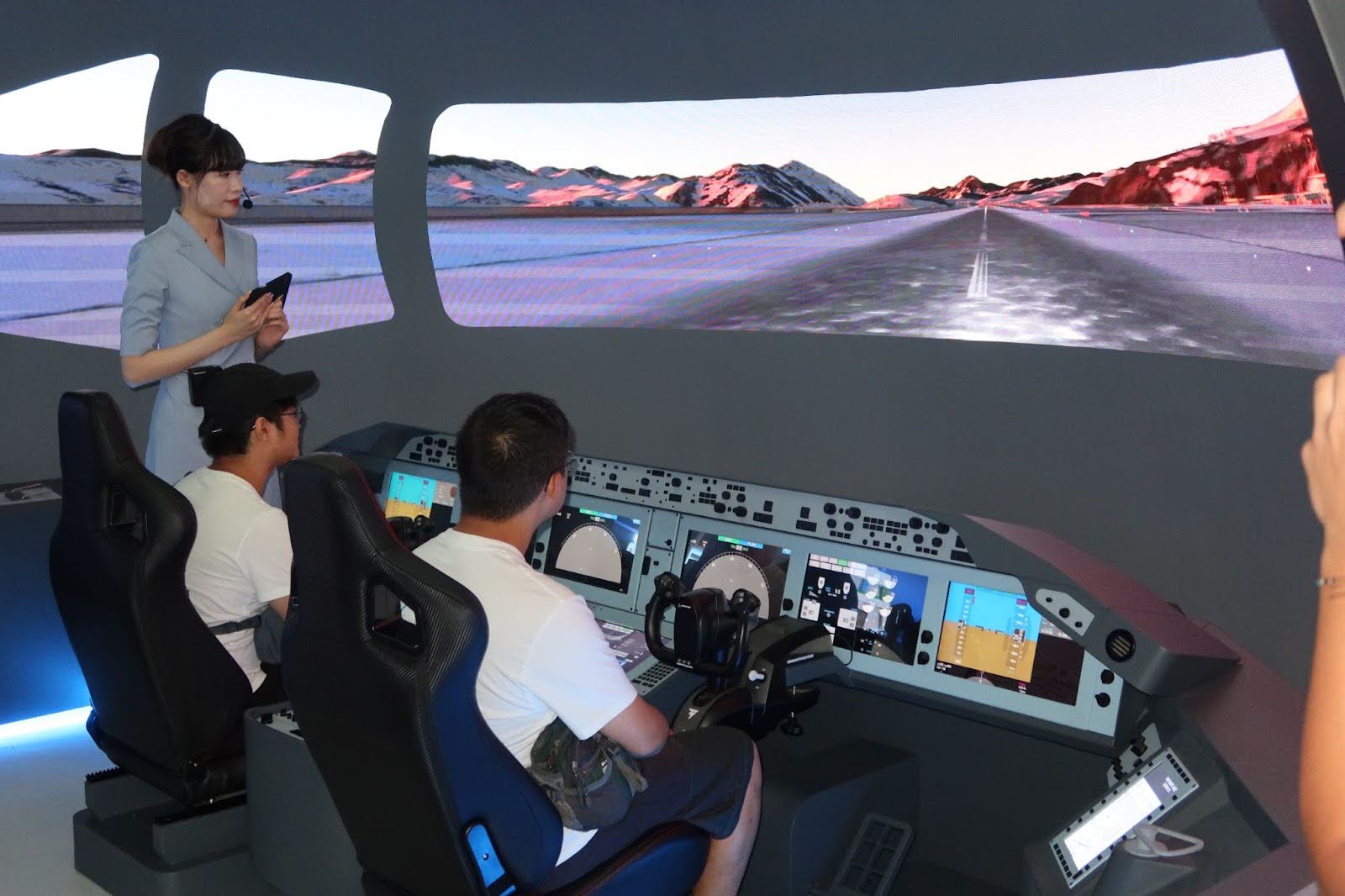





1️⃣ Company Snapshot
Tencent 腾讯控股有限公司
- Founded: 1998 · Headquartered in Shenzhen, China
- 2023 Revenue: $85 billion · Net Profit: $27 billion · Market Cap: $400+ billion
- China’s largest tech conglomerate, anchored by WeChat’s 1.3 billion users, mobile gaming giants like Honor of Kings and PUBG Mobile, and fintech leadership with WeChat Pay
- Leader in AI, cloud computing, metaverse development, and strategic investments globally (e.g., Riot Games, Epic Games)
- 🔗 https://www.tencent.com
- 📌 “The super-app ecosystem that powers everyday life and smart cities in China”
2️⃣ Why This Company Matters to SEE China
Tencent is fundamental to China’s digital infrastructure, showcasing how a super-app can integrate social, entertainment, payment, healthcare, and government services seamlessly. As a core partner in national digital and smart city initiatives, Tencent illustrates China’s top-down coordination in urban tech and AI innovation.
3️⃣ Industry Context & Comparison
Key Driver | Tencent (China, Shanghai Implementation) | Google (U.S. Urban Tech) |
Productivity + Market Reform | WeChat mini-programs and Tencent Cloud enable tightly integrated urban services | U.S. digital wallets and cloud platforms are fragmented with limited integration |
Long-Term Strategic Planning | Central partner in “Digital China” and “Smart City” initiatives | Smart city projects are decentralized and locally driven, with limited federal coordination |
Institutional Advantage | State-supported systemic digital integration and large-scale deployment | Fragmented urban tech ecosystems with multiple local governance layers |
4️⃣ Student Field Highlights
📷 Photos: WeChat mini-program demos / 3D virtual meeting setups / Tencent AI labs
💬 Quote: “Tencent’s integration of payment, healthcare, and social tools feels like a digital city in one app.”
5️⃣ Student Takeaways
“WeChat’s all-in-one model redefines how people live, work, and play digitally.”
“Tencent’s AI and virtual reality demos showed how tech powers both entertainment and enterprise.”
“China’s top-down planning really accelerates smart city tech deployment compared to the U.S.”
6️⃣ Explore More
- 📄 Related: “Super-apps and Smart Cities: China’s Digital Future”
- 🔁 Compare with: Google Urban Tech + U.S. Smart City Initiatives
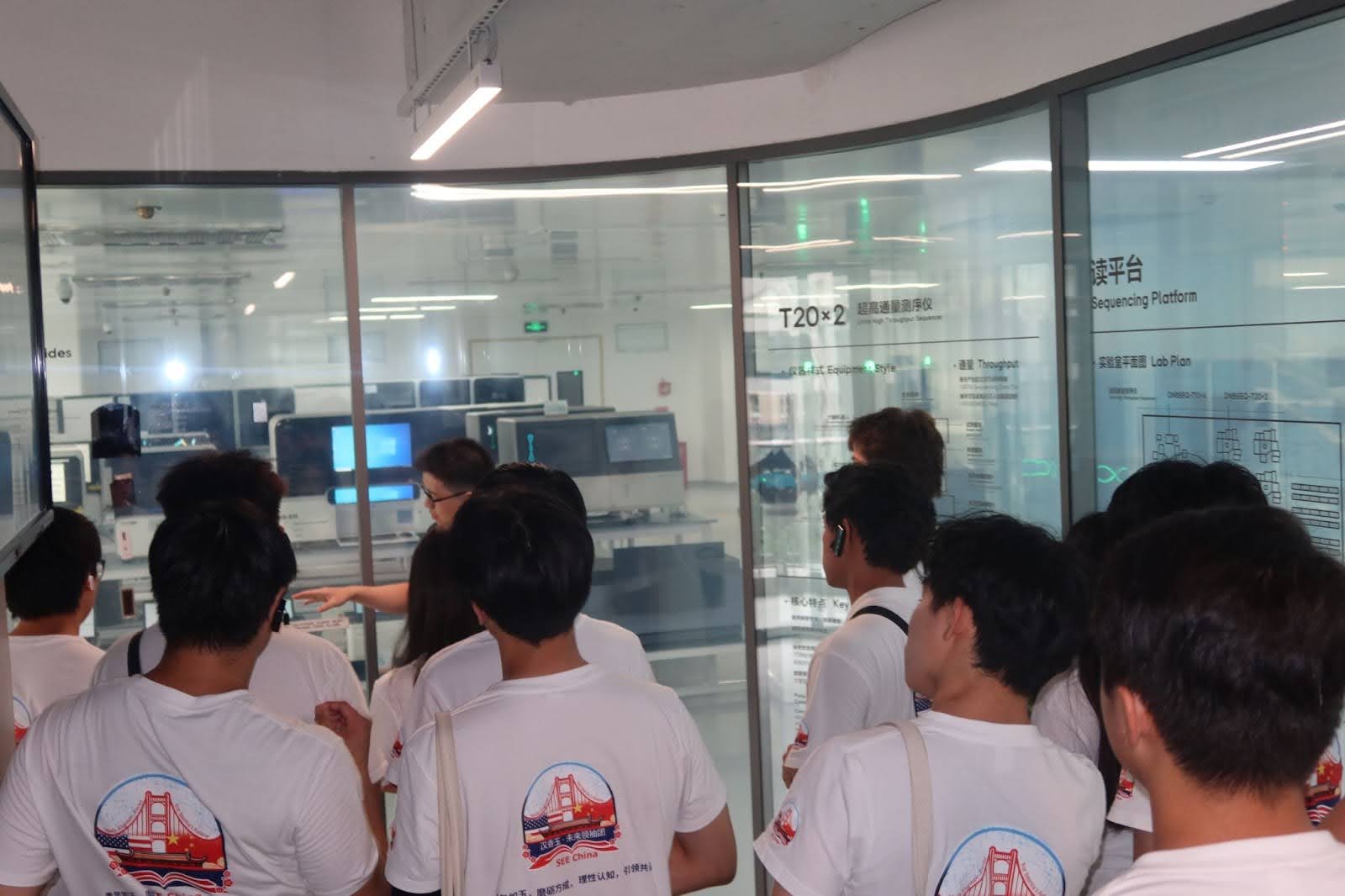






1️⃣ Company Snapshot
BGI Group 华大基因
- Founded: 1999 · Headquartered in Shenzhen, China
- 2023 Revenue: $3.2 billion
- Leading genomics and biotechnology company with massive sequencing capacity and cost-efficient solutions
- Key player in precision medicine, genetic testing, agricultural genomics, and global projects like the Earth BioGenome Project and COVID-19 diagnostics
- 🔗 https://www.bgi.com/global
- 📌 “Transforming genomics into China’s national health infrastructure”
2️⃣ Why This Company Matters to SEE China
BGI exemplifies China’s approach to integrating genomics within national health strategy through state-aligned science platforms. Acting as a data integrator and rapid responder, BGI contrasts with U.S. peers by leveraging centralized data sharing, government partnerships, and strategic planning—illustrating China’s coordinated biomedical innovation system.
3️⃣ Industry Context & Comparison
Key Driver | BGI (China) | Illumina (U.S.) |
Productivity + Market Reform | Integrated genome databases; cost-effective sequencing; standardized data sharing | Fragmented data; scattered private labs; strict IP limits data openness |
Long-Term Strategic Planning | Government-aligned precision medicine initiatives with rapid coordination | Longer funding cycles; less direct government guidance; competitive landscape |
Institutional Advantage | Top-down, coordinated planning and funding | Decentralized, market-driven, fragmented biomedical funding |
4️⃣ Student Field Highlights
📷 Photos: Genomic sequencing lab / ethical discussion session / BGI global project maps
💬 Quote: “BGI showed us the power of integrating data and policy for health innovation.”
5️⃣ Student Takeaways
“Understanding BGI helped me see how China uses science to build national infrastructure.”
“The ethical debates made me think differently about data privacy in biotech.”
“BGI’s scale and government ties contrast with the more commercial U.S. model.”
6️⃣ Explore More
- 📄 Related: “Genomics and National Health Infrastructure: China vs. U.S.”
- 🔁 Compare with: Illumina + U.S. Genomics Industry





1️⃣ Company Snapshot
Deep Robotics (深度机器人)
- Founded: 2016 * Hangzhou, China
- Specialized in quadruped robotics (仿生四足机器人) for industrial inspection, public safety, and emergency response
- First Chinese company to mass-produce commercial quadruped robots – deployed in hazardous environments, power plants, and disaster zones
- 🔗 http://www.deeprobotics.cn
- 📌 “Pioneering agile robotics for China’s industrial and public sector needs.”
2️⃣ Why This Company Matters to SEE China
Deep Robotics reflects China’s push to indigenize advanced robotics for infrastructure and security applications. Unlike U.S. peers (e.g., Boston Dynamics), it emphasizes cost-effective, ruggedized robots aligned with state priorities like “smart manufacturing” (智能制造) and “emergency tech reserves” (应急技术装备). Its partnerships with police and state grid operators showcase how Chinese robotics firms leverage state-guided demand.
3️⃣ Industry Context & Comparison
Key Driver | Deep Robotics (China) | Boston Dynamics (U.S.) |
Productivity + Market Reform | High-volume, low-cost production for industrial/logistics use; integrated with China’s “robot+” supply chain ecosystem | Premium-priced, low-volume R&D prototypes; reliant on niche markets (e.g., entertainment, military) |
Long-Term Strategic Planning | Aligned with Made in China 2025 robotics goals; state-backed pilot projects (e.g., power grid inspections, disaster relief) | Ad-hoc commercialization (e.g., Hyundai acquisition); no centralized national strategy guiding development |
Institutional Advantage | Access to state procurement (e.g., public safety contracts); subsidies for localization of core components (motors, LiDAR) | Decentralized innovation; dependent on private capital and defense contracts (e.g., DARPA) |
4️⃣ Student Field Highlights
📷 Photos: Robot demo in a mock disaster zone / engineers testing payload adaptability / workshop on AI gait optimization
💬 Quote: “Deep Robotics doesn’t just build robots—they build tools for China’s infrastructure resilience.”
5️⃣ Student Takeaways
“China’s focus on ‘practical’ robotics contrasts with U.S. hype around humanoid robots.”
“Seeing robots inspect high-voltage lines made me rethink automation in critical infrastructure.”
“Deep Robotics’ state ties mirror China’s model of tech serving national objectives.”
6️⃣ Explore More
- 📄 Related: “Quadruped Robots in China: Industrial Policy in Action”
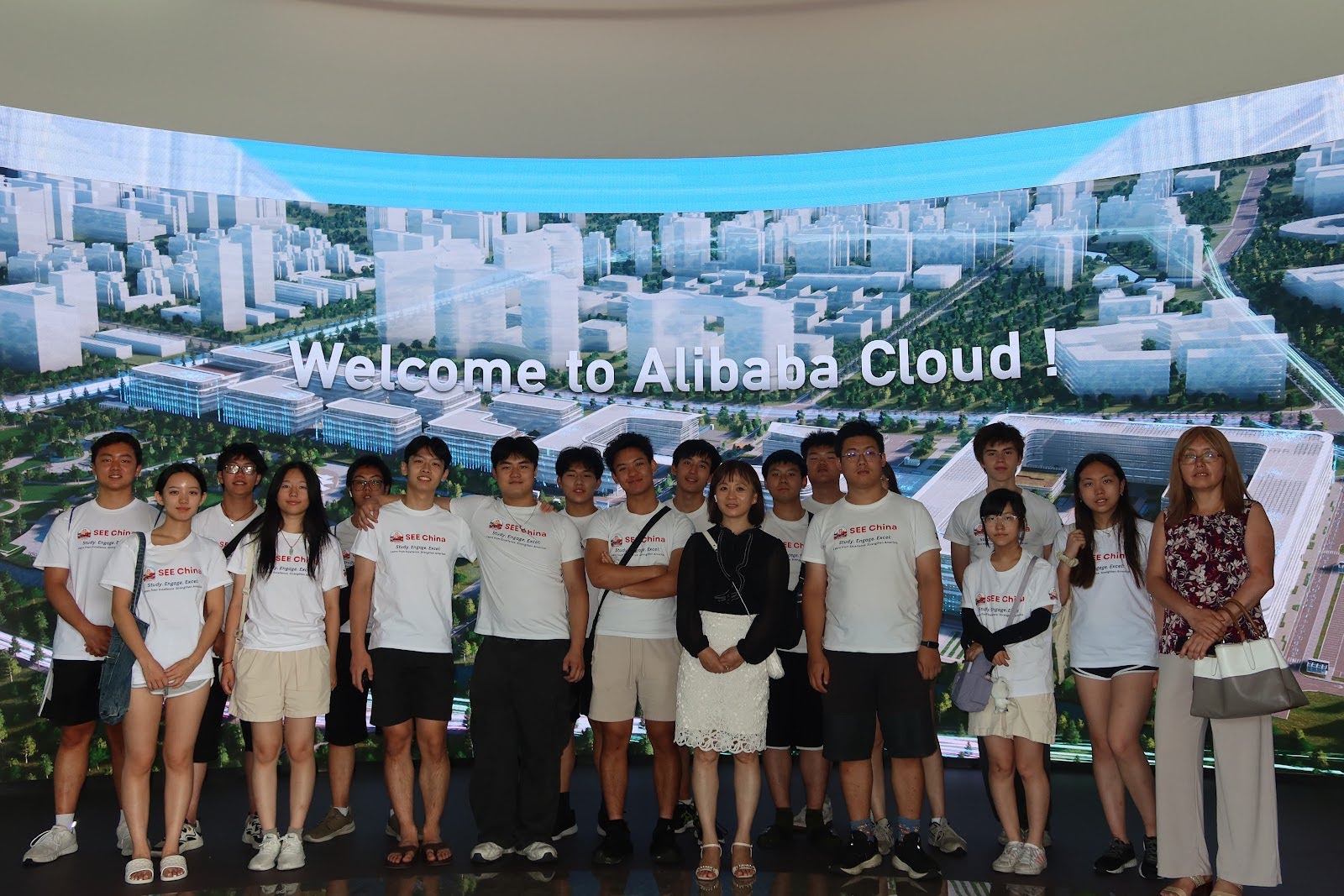
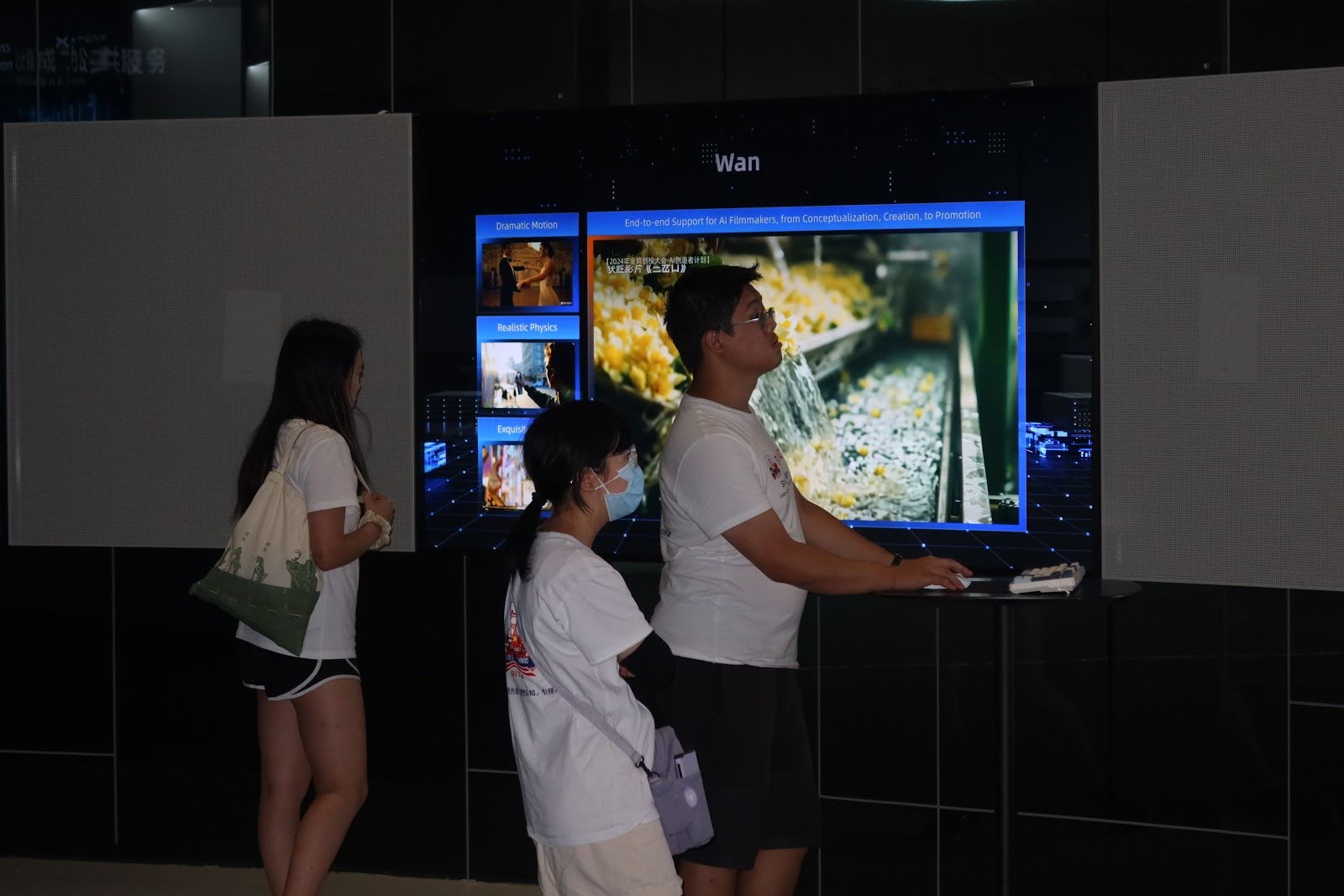
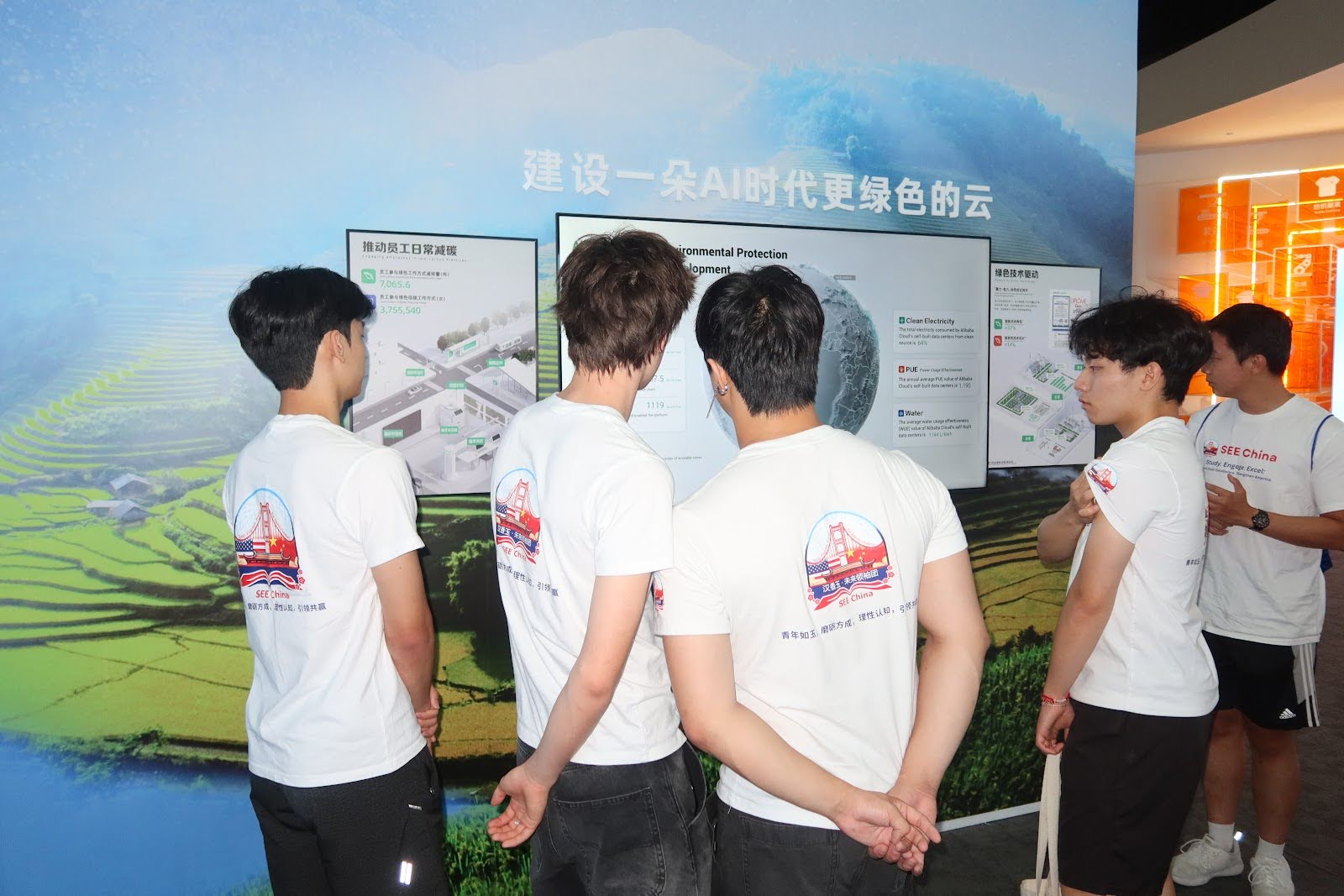
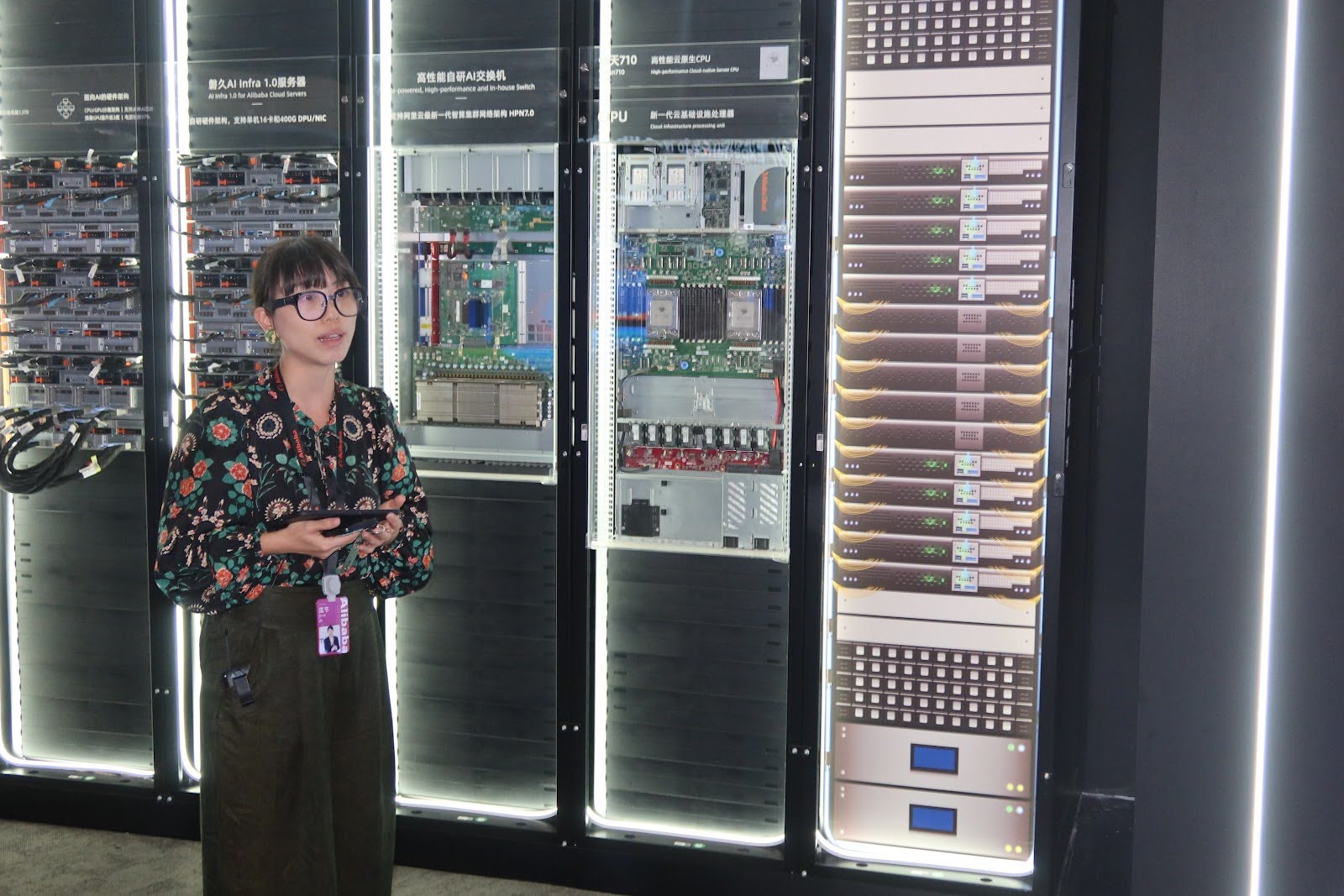
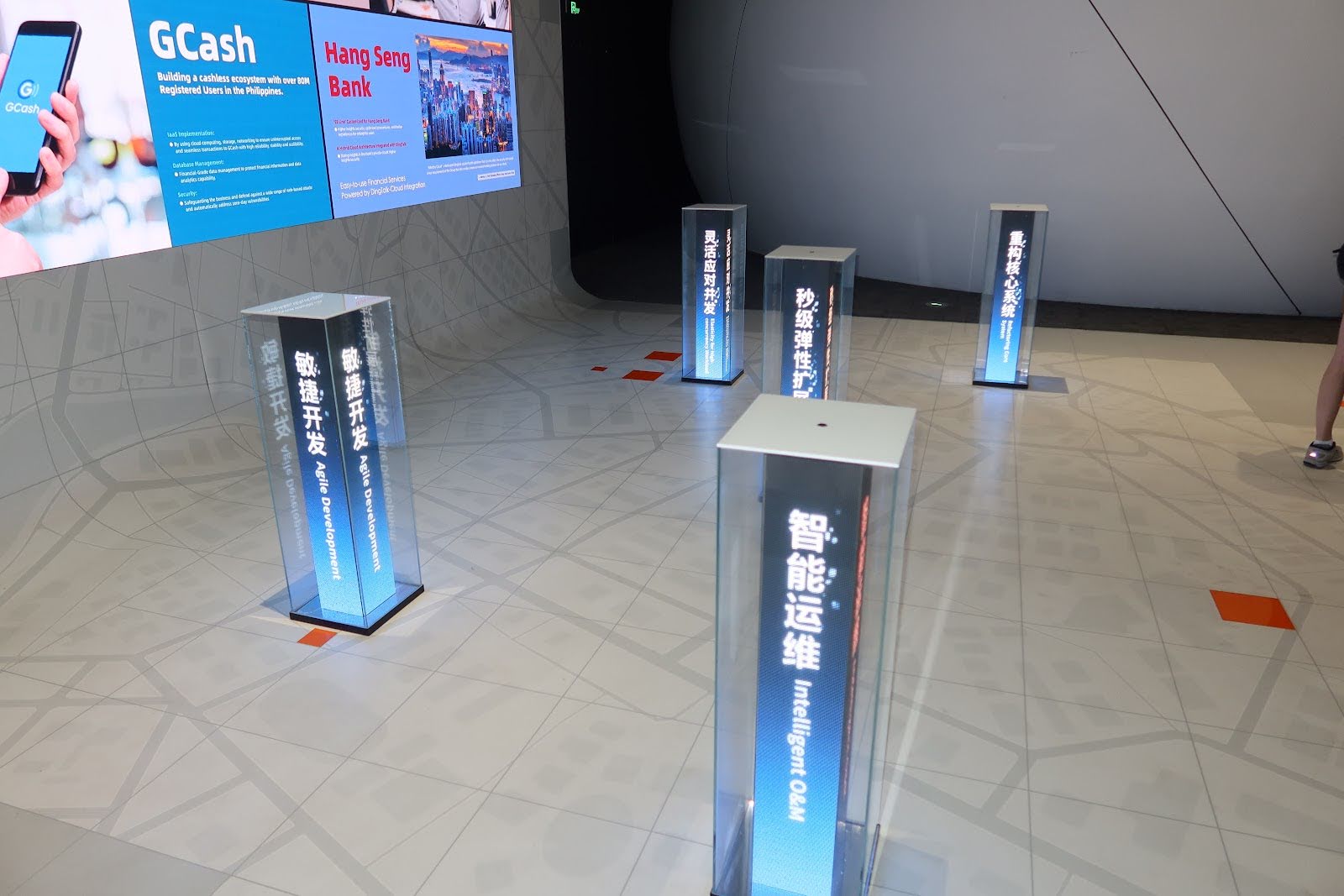






1️⃣ Company Snapshot
Alibaba Cloud (阿里云)
Founded: 2009 · Hangzhou, China
China’s largest cloud computing and AI service provider, powering everything from rural education to urban governance.
Core products include the Tongyi Qianwen large language model, AI-generated media tools, and enterprise cloud platforms for logistics, finance, and e-commerce.
🔗 alibabacloud.com
📌 “AI infrastructure for China’s digital future.”
2️⃣ Why This Company Matters to SEE China
Alibaba Cloud reflects China’s ambition to create sovereign AI ecosystems at scale. Unlike U.S. firms (OpenAI, AWS), which focus on frontier research and developer tools, Aliyun is designed for mass rollout—powering public services, rural schools, hospitals, and SMEs. Its AI is deeply embedded in China’s daily life, offering students a look at how cloud infrastructure can drive national digital transformation from the bottom up.
3️⃣ Industry Context & Comparison
Key Driver | Alibaba Cloud (China) | AWS/OpenAI (U.S.) |
National Strategy | Backbone for e-gov, rural education, digital public infrastructure | Market-driven growth; limited public-sector role |
Tech Ecosystem | Integrated with Taobao, DingTalk, and provincial-level platforms | Modular services and APIs; optimized for startups and developers |
Data & Compliance | Collaborates with regulators to align AI with national standards | Privacy-first, regulatory arms-length approach |
Access Model | AI tools embedded in gov apps, rural kits, and school platforms | Access limited to developers and enterprise clients |
4️⃣ Student Field Highlights
📷 Photos: Tongyi Qianwen demo / rural school AI toolkits / comparison of ChatGPT and Tongyi outputs
💬 Quote: “Aliyun makes AI usable, not just impressive.”
5️⃣ Student Takeaways
“Unlike OpenAI, Aliyun is built for mass adoption and regulation.”
“Seeing AI used in rural China was eye-opening.”
“China sees AI as public utility, not just private profit.”
6️⃣ Explore More
📄 Related: “Tongyi vs. ChatGPT: A Comparative Student Test”
🔁 Compare with: OpenAI, AWS Bedrock, Google Cloud AI
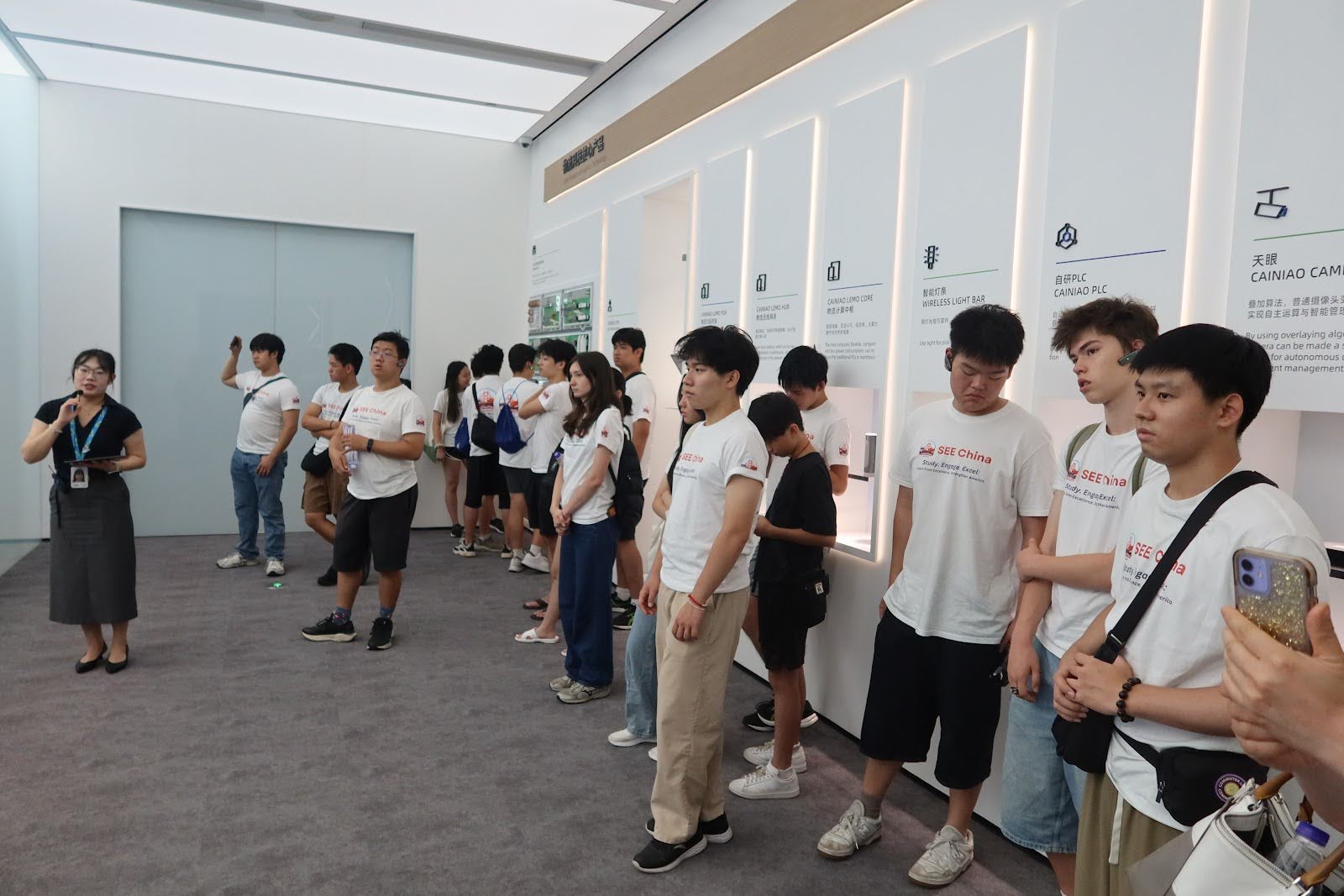
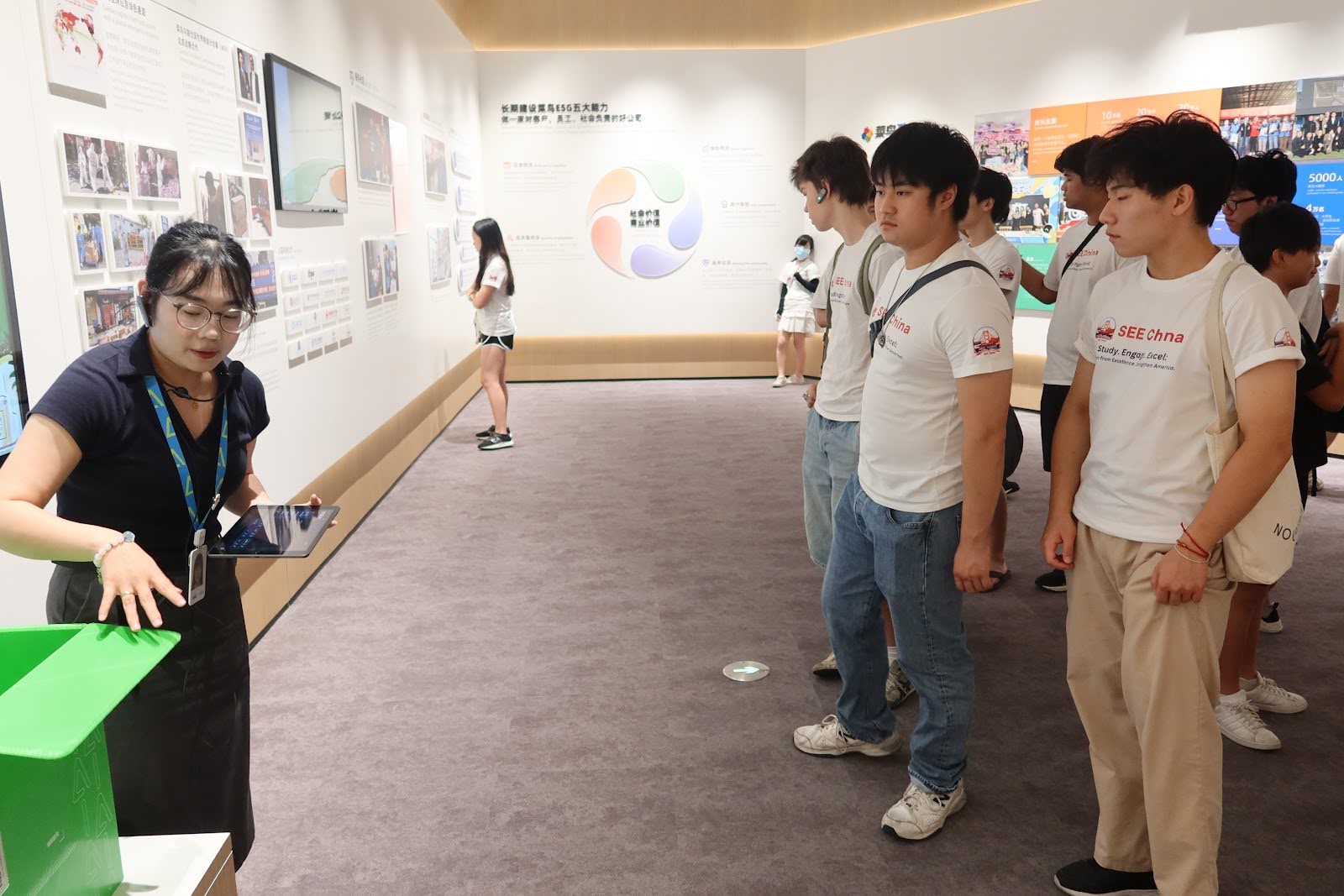
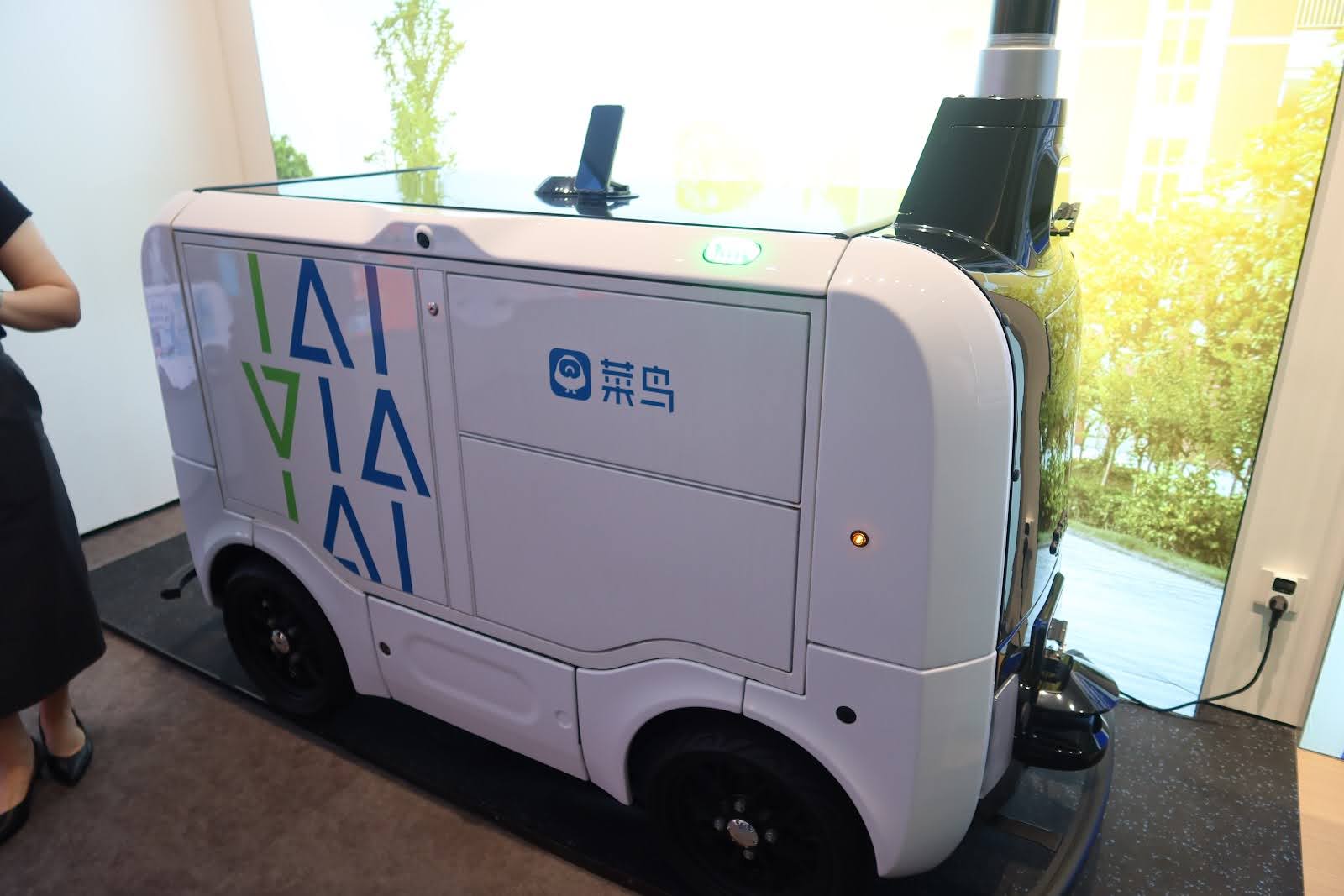
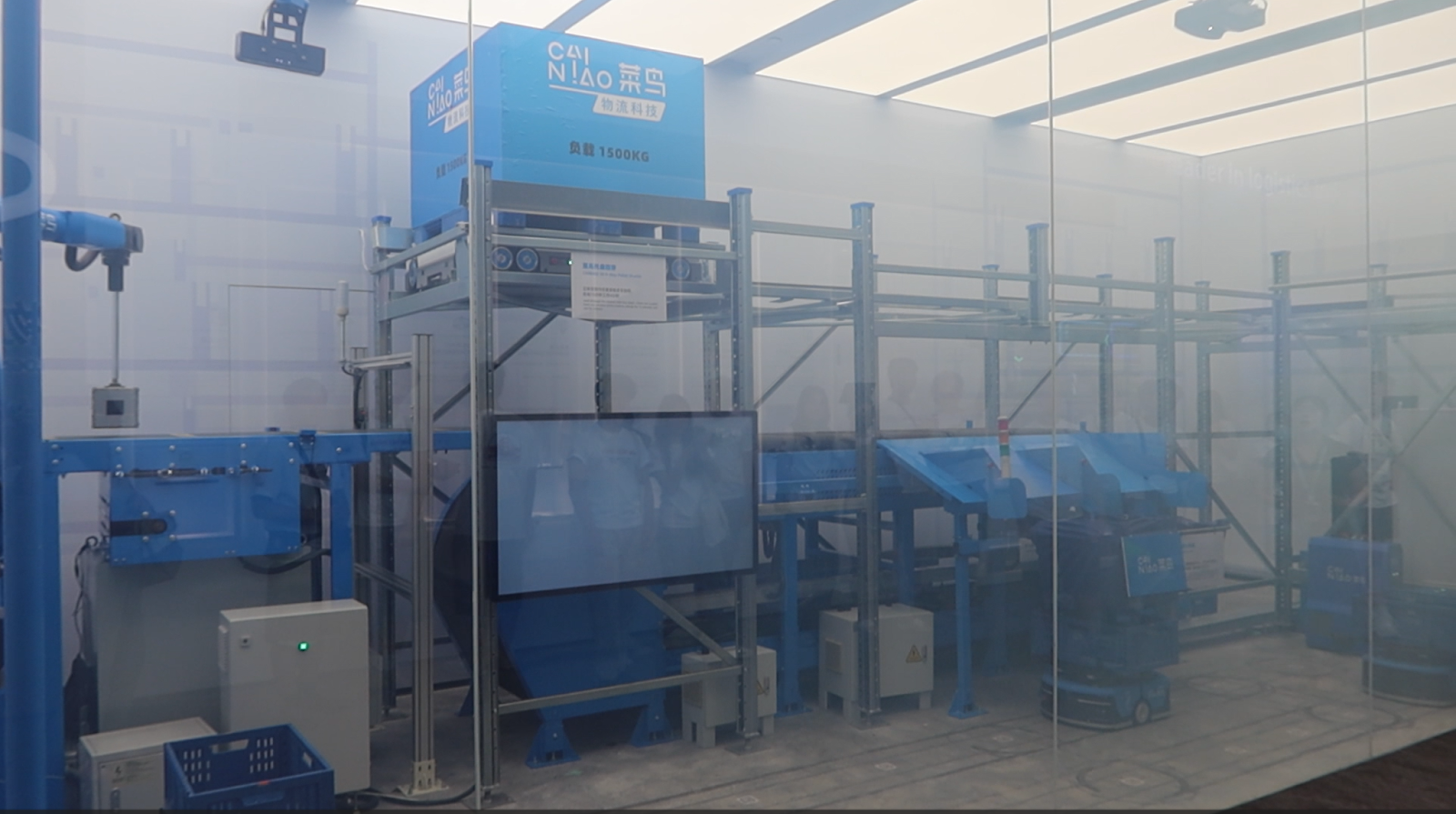






1️⃣ Company Snapshot
Cainiao Smart Logistics Network (菜鸟网络)
Founded: 2013 · Hangzhou, China
Alibaba’s logistics platform optimizing e-commerce fulfillment, cross-border shipping, and smart warehousing.
Known for innovations like AI-powered sorting, delivery drones, campus robots, and smart lockers across cities and rural areas.
🔗 cainiao.com
📌 “Digitizing the flow of everything, everywhere.”
2️⃣ Why This Company Matters to SEE China
Cainiao shows how China redefines logistics as digital infrastructure. While Amazon builds for internal needs, Cainiao operates an open platform for 3rd-party sellers, SMEs, and global partners. Its AI-first, automation-heavy approach helps scale logistics to match China’s e-commerce boom—while also bringing delivery to remote villages and new markets abroad.
3️⃣ Industry Context & Comparison
Key Driver | Cainiao (China) | Amazon Logistics (U.S.) |
Last Mile Innovation | AI sorting, robot delivery, campus lockers | Human-led delivery with route optimization |
Platform Positioning | Neutral logistics backbone for Alibaba + 3rd-party sellers | In-house logistics system for Amazon retail |
Global Reach | Bonded hubs in Europe, SEA; Alibaba’s global e-commerce tie-in | Primarily U.S.-focused; limited international fulfillment reach |
Infrastructure Role | Tied to China’s smart logistics policy and urban freight strategy | Privately funded with efficiency-driven logistics stack |
4️⃣ Student Field Highlights
📷 Photos: robot delivery in university campus / AI sorting center / drone package flight demo
💬 Quote: “Cainiao is logistics with Chinese characteristics.”
5️⃣ Student Takeaways
“China’s logistics is more automated, more public-facing, and more systemic.”
“Cainiao’s openness contrasts with Amazon’s vertical stack.”
“Smart logistics may be China’s strongest silent export.”
📄 Related: “From Parcel to Platform: Cainiao and China’s Logistics Revolution”
🔁 Compare with: Amazon Logistics, FedEx, JD Logistics






1️⃣ Company Snapshot
Alipay (蚂蚁集团旗下)
Founded: 2004 · Hangzhou, China
The world’s largest digital payments platform, serving over 1 billion users across finance, health, and public services.
More than a wallet—Alipay integrates microloans, insurance, credit scoring, and government services into a single app.
🔗 alipay.com
📌 “Re-imagining finance for the mobile-first era.”
2️⃣ Why This Company Matters to SEE China
Alipay shows how China’s fintech model goes beyond transactions—blending financial services with daily life and public governance. As a super app, Alipay enables everything from paying bills to booking hospital appointments. In contrast to U.S. firms like Visa, which focus on cards and merchants, Alipay reflects China’s “finance as infrastructure” approach.
3️⃣ Industry Context & Comparison
Key Driver | Alipay (China) | Visa (U.S.) |
Financial Inclusion | Microloans, rural QR access, app-based credit scoring | Bank-issued credit card access |
Infrastructure Model | All-in-one super app with gov, health, and tax integrations | Siloed systems: banks, apps, and card networks |
Tech Deployment | AI-powered fraud control, smart credit, social services | Transaction-focused with limited AI infrastructure |
Regulation | Aligns with central bank and digital yuan frameworks | Private, profit-driven, federally overseen |
4️⃣ Student Field Highlights
📷 Photos: mobile clinic check-in via Alipay / Sesame Credit experience booth / QR payments in rural setting
💬 Quote: “Alipay is where fintech meets social engineering.”
5️⃣ Student Takeaways
“Alipay is a public service platform wrapped in a commercial skin.”
“Compared to Visa, Alipay feels like infrastructure, not just a payment tool.”
“China’s digital finance blends convenience, control, and central planning.”
📄 Related: “Alipay’s Super App Model: What the U.S. Can’t Copy”
🔁 Compare with: Visa, Apple Pay, Venmo
